Heritability of DNA-damage-induced apoptosis and its relationship with age in lymphocytes from female twins
- PMID: 16819540
- PMCID: PMC2360659
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603257
Heritability of DNA-damage-induced apoptosis and its relationship with age in lymphocytes from female twins
Abstract
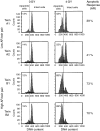
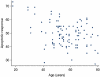
Apoptosis is a physiological form of cell death important in normal processes such as morphogenesis and the functioning of the immune system. In addition, defects in the apoptotic process play a major role in a number of important areas of disease, such as autoimmune diseases and cancer. DNA-damage-induced apoptosis plays a vital role in the maintenance of genomic stability by the removal of damaged cells. Previous studies of the apoptotic response (AR) to radiation-induced DNA damage of lymphoid cells from individuals carrying germline TP53 mutations have demonstrated a defective AR compared with normal controls. We have also previously demonstrated that AR is reduced as individuals age. Results from the current study on 108 twins aged 18-80 years confirm these earlier findings that the AR of lymphoid cells to DNA damage is significantly reduced with increasing age. In addition this twin study shows, for the first time, that DNA-damage-induced AR has a strong degree of heritability of 81% (95% confidence interval 67-89%). The vital role of DNA-damage-induced apoptosis in maintaining genetic stability, its relationship with age and its strong heritability underline the importance of this area of biology and suggest areas for further study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Apoptosis, ageing and cancer susceptibility.Br J Cancer. 2003 Feb 24;88(4):487-90. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600767. Br J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12592359 Free PMC article.
-
A possible screening test for inherited p53-related defects based on the apoptotic response of peripheral blood lymphocytes to DNA damage.Br J Cancer. 1995 Sep;72(3):654-62. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.390. Br J Cancer. 1995. PMID: 7669577 Free PMC article.
-
Basal DNA damage in individual human lymphocytes with age.Mutat Res. 1991 Jan;256(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/0921-8734(91)90026-8. Mutat Res. 1991. PMID: 1944382
-
The immune system in the elderly: activation-induced and damage-induced apoptosis.Immunol Res. 2004;30(1):81-94. doi: 10.1385/IR:30:1:081. Immunol Res. 2004. PMID: 15258312 Review.
-
What does cell death have to do with aging?J Am Geriatr Soc. 1997 Sep;45(9):1140-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1997.tb05981.x. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1997. PMID: 9288026 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemotherapeutic-induced apoptosis: a phenotype for pharmacogenomics studies.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2011 Aug;21(8):476-88. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e3283481967. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21642893 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and environmental influence on DNA strand break repair: a twin study.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2013 Jul;54(6):414-20. doi: 10.1002/em.21791. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2013. PMID: 23798034 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic determinants of neuronal vulnerability to apoptosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Jan;70(1):71-88. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1029-y. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22695677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of the Acute or Late Radiation Toxicity Effects in Radiotherapy Patients Using Ex Vivo Induced Biodosimetric Markers: A Review.J Pers Med. 2020 Dec 16;10(4):285. doi: 10.3390/jpm10040285. J Pers Med. 2020. PMID: 33339312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heritability of susceptibility to ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis of human lymphocyte subpopulations.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007 Jul 15;68(4):1169-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.03.050. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007. PMID: 17637392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrew T, Hart DJ, Snieder H, de Lange M, Spector TD (2001) Are twins and singletons comparable? A study of disease-related and lifestyle characteristics in women. Twins Res 4: 464–477 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

