Inhibition of insulin receptor isoform-A signalling restores sensitivity to gefitinib in previously de novo resistant colon cancer cells
- PMID: 16819546
- PMCID: PMC2360620
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603237
Inhibition of insulin receptor isoform-A signalling restores sensitivity to gefitinib in previously de novo resistant colon cancer cells
Abstract
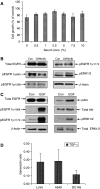
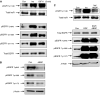
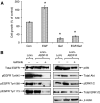
Resistance to antiepidermal growth factor (EGFR) strategies is an emerging clinical problem. Using human colorectal cancer (CRC) cells, we evaluated the involvement of the insulin receptor isoform-A (InsR-A) in de novo resistance to gefitinib, an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Challenging the EGFR positive LoVo cells with gefitinib (1 microM) resulted in a small ( approximately 18%) inhibition of cell growth and although a modest reduction in phospho (p)EGFR Tyr845 was seen, pEGFR at residues -Tyr1068 and -Tyr1173 were unchanged. LoVo cells produced unprocessed pro-IGF-1R protein, substantial levels of IGF-II mRNA and mature InsR protein, consisting mainly of the InsR-A isoform. Insulin and IGF-II promoted cell growth and pEGFR Tyr845, Tyr1068 and Tyr1173 activity and conversely, the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R)/InsR inhibitor ABDP (1 muM) inhibited growth and reduced pEGFR activity at all three tyrosine residues. pInsR and pAkt levels were increased after gefitinib treatment. Blocking of pInsR with ABDP enabled gefitinib to markedly reduce pEGFR Tyr845, Tyr1068 and Tyr1173. Short-term gefitinib/ABDP dual treatment was more effective than either agent alone and chronic exposure to this combination resulted in total cell loss after 9 weeks, preventing acquisition of resistance to ABDP. LoVo cells with acquired resistance to ABDP were acutely sensitive to gefitinib. We concluded that InsR-A reduces sensitivity to gefitinib in LoVo CRC cells, thus its co-targeting alongside EGFR can improve the anti-tumour effect of gefitinib.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor is implicated in resistance to the cytostatic effect of gefitinib in colorectal cancer cells.J Gastrointest Surg. 2011 Jun;15(6):942-57. doi: 10.1007/s11605-011-1504-z. Epub 2011 Apr 9. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011. PMID: 21479670
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signalling and acquired resistance to gefitinib (ZD1839; Iressa) in human breast and prostate cancer cells.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2004 Dec;11(4):793-814. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.00799. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15613453
-
InsR/IGF1R Pathway Mediates Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors in Glioblastoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Apr 1;22(7):1767-76. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1677. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26561558 Free PMC article.
-
Development of strategies for the use of anti-growth factor treatments.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005 Jul;12 Suppl 1:S173-82. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.01004. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16113094 Review.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2/insulin-like growth factor receptor signalling and oestrogen receptor activity in clinical breast cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005 Jul;12 Suppl 1:S99-S111. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.01005. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16113104 Review.
Cited by
-
Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of Linsitinib (OSI-906) and Erlotinib in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jun 15;22(12):2897-907. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2218. Epub 2016 Feb 1. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26831715 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Growth factor signalling in endocrine and anti-growth factor resistant breast cancer.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2007 Sep;8(3):241-53. doi: 10.1007/s11154-007-9033-5. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2007. PMID: 17486454 Review.
-
Anticancer activity of the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor antagonist, ganitumab, in combination with the death receptor 5 agonist, conatumumab.Target Oncol. 2015 Mar;10(1):65-76. doi: 10.1007/s11523-014-0315-z. Epub 2014 May 11. Target Oncol. 2015. PMID: 24816908 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Disruption of insulin receptor function inhibits proliferation in endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells.Oncogene. 2016 Aug 11;35(32):4235-43. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.488. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26876199 Free PMC article.
-
Altered expression of insulin receptor isoforms in breast cancer.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26177. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026177. Epub 2011 Oct 26. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22046260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams TE, McKern NM, Ward CW (2004) Signalling by the Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor: interplay with the epidermal growth factor receptor. Growth Factors 22(2): 89–95 - PubMed
-
- Arteaga CL (2002) Epidermal growth factor receptor dependence in human tumours: more than just expression. Oncologist 7(Suppl 4): 31–39 - PubMed
-
- Chakravarti A, Loeffler JS, Dyson NJ (2002) Insulin-like growth factor receptor I mediates resistance to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapy in primary human glioblastome cells through continued activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling. Cancer Res 62: 200–207 - PubMed
-
- Cho CD, Fisher GA, Halsey J, Sikic BI (2005) Phase I study of gefitinib, oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin (IFOX) in patients with advanced solid malignancies. Invest New Drugs 23: 1–7 - PubMed
-
- Ciardiello F, Caputo R, Bianco R, Damiano V, Fontanini G, Cuccato S, De Placido S, Bianco AR, Tortora G (2001) Inhibition of growth factor production and angiogenesis in human cancer cells by ZD1839 (Iressa), a selective epidermal growth factor receptor-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res 7: 1459–1465 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

