Endoscopic palliation of malignant dysphagia: a challenging task in inoperable oesophageal cancer
- PMID: 16820062
- PMCID: PMC1540418
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7819-4-38
Endoscopic palliation of malignant dysphagia: a challenging task in inoperable oesophageal cancer
Abstract
Background: The main goal when managing patients with inoperable oesophageal cancer is to restore and maintain their oral nutrition. The aim of the present study was to assess the value of endoscopic palliation of dysphagia in patients with oesophageal cancer, who either due to advanced stage of the disease or co-morbidity are not suitable for surgery.
Patients and methods: All the endoscopic palliative procedures performed over a 5-year period in our unit were retrospectively reviewed. Dilatation and insertion of self-expandable metal stents (SEMS) were mainly used for tight circumferential strictures whilst ablation with Nd-YAG laser was used for exophytic lesions. All procedures were performed under sedation.
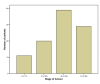
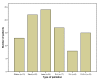
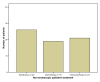
Results: Overall 249 palliative procedures were performed in 59 men and 40 women, with a median age of 73 years (range 35-93). The median number of sessions per patient was 2 (range 1-13 sessions). Palliation involved laser ablation alone in 24%, stent insertion alone in 22% and dilatation alone in 13% of the patients. In 41% of the patients, a combination of the above palliative techniques was applied. A total of 45 SEMS were inserted. One third of the patients did not receive any other palliative treatment, whilst the rest received chemotherapy, radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy. Swallowing was maintained in all patients up to death. Four oesophageal perforations were encountered; two were fatal whilst the other two were successfully treated with covered stent insertion and conservative treatment. The median survival from diagnosis was 10.5 months (range 0.5-83 months) and the median survival from 1st palliation was 5 months (range 0.5-68.5 months).
Conclusion: Endoscopic interventions are effective and relatively safe palliative modalities for patients with oesophageal cancer. It is possible to adequately palliate almost all cases of malignant dysphagia. This is achieved by expertise in combination treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Self-expanding metal stents for palliation of malignant oesophageal obstruction].Magy Seb. 2009 Apr;62(2):59-66. doi: 10.1556/MaSeb.62.2009.2.2. Magy Seb. 2009. PMID: 19386565 Hungarian.
-
Use of covered expandable metal stents in the treatment of oesophageal carcinoma and tracheo-oesophageal fistula.Br J Surg. 1996 Oct;83(10):1417-8. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800831030. Br J Surg. 1996. PMID: 8944460
-
The cost effectiveness of metal oesophageal stenting in malignant disease compared with conventional therapy.Clin Radiol. 1999 Apr;54(4):212-5. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(99)91153-4. Clin Radiol. 1999. PMID: 10210338
-
Self-expanding metal stent insertion for inoperable esophageal carcinoma in Belfast: an audit of outcomes and literature review.Dis Esophagus. 2011 Nov;24(8):569-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2011.01188.x. Epub 2011 Mar 18. Dis Esophagus. 2011. PMID: 21418125 Review.
-
Palliation of malignant dysphagia from oesophageal cancer. Rotterdam Oesophageal Tumor Study Group.Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1998;225:75-84. doi: 10.1080/003655298750027272. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1998. PMID: 9515757 Review.
Cited by
-
Endoscopic stenting and concurrent chemoradiotherapy for advanced esophageal cancer: a case-control study.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Mar 28;18(12):1404-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i12.1404. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22493556 Free PMC article.
-
Palliation of malignant esophageal obstruction and fistulas with self expandable metallic stents.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Dec 7;16(45):5739-45. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i45.5739. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 21128325 Free PMC article.
-
Combined chemotherapy plus endostar with sequential stereotactic radiotherapy as salvage treatment for recurrent esophageal cancer with severe dyspnea: A case report and review of the literature.Oncol Lett. 2014 Jul;8(1):291-294. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2087. Epub 2014 Apr 25. Oncol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24959263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cancer Stats Monograph 2004. Cancer incidence, survival and mortality in the UK and EU. Cancer Research UK;
-
- Müller JM, Erasmi H, Stelzner , et al. Surgical therapy of oesophageal carcinoma. Br J Surg. 1990;77:845–57. - PubMed
-
- Earlam R, Cuhna-Melo JR. Oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Critical review of surgery. Br J Surg. 1980;67:381–90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources