Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in hamster and human pancreatic neoplasia
- PMID: 16820089
- PMCID: PMC1601471
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.04700
Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in hamster and human pancreatic neoplasia
Abstract
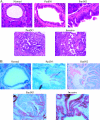
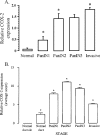
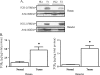
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) has been implicated in the development of gastrointestinal malignancies. The aim of the present study was to determine COX-2 expression/activity throughout stages of experimental and human pancreatic neoplasia. COX-2 immunohistochemistry was performed in pancreata of hamsters subjected to the carcinogen N-nitrosobis-(2-oxopropyl)amine (BOP) and in human pancreatic tumors. COX-2 activity was determined by prostaglandin E2 assay in tumor versus matched normal pancreatic tissues. The activity of the COX inhibitor sulindac was tested in the PC-1 hamster pancreatic cancer model. COX-2 expression was elevated in all pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasias (PanINs) and adenocarcinomas. In BOP-treated hamsters, there were significant progressive elevations in COX-2 expression throughout pancreatic tumorigenesis. In human samples, peak COX-2 expression occurred in PanIN2 lesions and remained moderately elevated in PanIN3 and adenocarcinoma tissues. COX-2 activity was significantly elevated in hamster and human pancreatic cancers compared to pair-matched normal pancreas. Furthermore, hamster pancreatic tumor engraftment/formation in the PC-1 hamster pancreatic cancer model was reduced 4.9-fold by oral administration of sulindac. Increased COX-2 expression is an early event in pancreatic carcinogeneses. The BOP-induced hamster carcinogenesis model is a representative model used to study the role of COX-2 in well-differentiated pancreatic tumorigenesis. COX inhibitors may have a role in preventing tumor engraftment/formation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Increased expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in N-nitrosobis(2-oxopropyl)amine-induced hamster pancreatic carcinogenesis and prevention of cancer development by ONO-1714, an iNOS inhibitor.Carcinogenesis. 2008 Aug;29(8):1608-13. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn152. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Carcinogenesis. 2008. PMID: 18567618
-
Increased cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human pancreatic carcinomas and cell lines: growth inhibition by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.Cancer Res. 1999 Sep 1;59(17):4356-62. Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10485483
-
Nitric oxide-donating aspirin prevents pancreatic cancer in a hamster tumor model.Cancer Res. 2006 Apr 15;66(8):4503-11. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3118. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16618778
-
Impact of cyclooxygenase-2 in breast cancer.Anticancer Res. 2011 Dec;31(12):4359-67. Anticancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22199301 Review.
-
Involvement of inflammatory factors in pancreatic carcinogenesis and preventive effects of anti-inflammatory agents.Semin Immunopathol. 2013 Mar;35(2):203-27. doi: 10.1007/s00281-012-0340-x. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Semin Immunopathol. 2013. PMID: 22955327 Review.
Cited by
-
EUS and pancreatic cyst fluid analysis: Is the juice worth the aqueeze?J Gastrointest Oncol. 2011 Dec;2(4):199-202. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2078-6891.2011.042. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2011. PMID: 22811851 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Suppressive effect of sulindac on branch duct-intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.J Gastroenterol. 2009;44(9):964-75. doi: 10.1007/s00535-009-0089-8. Epub 2009 Jun 18. J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19536452 Clinical Trial.
-
Oncolytic adenovirus expressing interferon alpha in a syngeneic Syrian hamster model for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.Surgery. 2015 May;157(5):888-98. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2015.01.006. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Surgery. 2015. PMID: 25731784 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental animal models of pancreatic carcinogenesis for prevention studies and their relevance to human disease.Cancers (Basel). 2011 Feb 9;3(1):582-602. doi: 10.3390/cancers3010582. Cancers (Basel). 2011. PMID: 24212630 Free PMC article.
-
Case-control study of aspirin use and risk of pancreatic cancer.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014 Jul;23(7):1254-63. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-13-1284. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014. PMID: 24969230 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;2:106–130. - PubMed
-
- McKenna S, Eatock M. The medical management of pancreatic cancer: a review. Oncologist. 2003;8:149–160. - PubMed
-
- Ding XZ, Tong WG, Adrian TE. Cyclooxygenases and lipoxygenases as potential targets for treatment of pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 2001;1:291–299. - PubMed
-
- Subbaramaiah K, Dannenberg AJ. Cyclooxygenase 2: a molecular target for cancer prevention and treatment. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24:96–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
