YtjE from Lactococcus lactis IL1403 Is a C-S lyase with alpha, gamma-elimination activity toward methionine
- PMID: 16820483
- PMCID: PMC1489307
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00712-06
YtjE from Lactococcus lactis IL1403 Is a C-S lyase with alpha, gamma-elimination activity toward methionine
Abstract
Cheese microbiota and the enzymatic conversion of methionine to volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) are important factors in flavor formation during cheese ripening and the foci in biotechnological approaches to flavor improvement. The product of ytjE of Lactococcus lactis IL1403, suggested to be a methionine-specific aminotransferase based on genome sequence analysis, was therefore investigated for its role in methionine catabolism. The ytjE gene from Lactococcus lactis IL1403 was cloned in Escherichia coli and overexpressed and purified as a recombinant protein. When tested, the YtjE protein did not exhibit a specific methionine aminotransferase activity. Instead, YtjE exhibited C-S lyase activity and shared homology with the MalY/PatC family of enzymes involved in the degradation of L-cysteine, L-cystine, and L-cystathionine. YtjE was also shown to exhibit alpha,gamma-elimination activity toward L-methionine. In addition, gas chromatographic-mass spectrometry analysis showed that YtjE activity resulted in the formation of H2S from L-cysteine and methanethiol (and its oxidized derivatives dimethyl disulfide and dimethyl trisulfide) from L-methionine. Given their significance in cheese flavor development, VSC production by YtjE could offer an additional approach for the development of cultures with optimized aromatic properties.
Figures
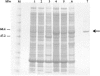
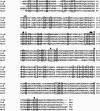
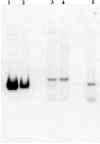

Similar articles
-
Heterologous production of methionine-gamma-lyase from Brevibacterium linens in Lactococcus lactis and formation of volatile sulfur compounds.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Apr;75(8):2326-32. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02417-08. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19251895 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and functional analysis of the gene encoding methionine-gamma-lyase in Brevibacterium linens.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Dec;70(12):7348-54. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.12.7348-7354.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15574935 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of sulfur compound production in lactic acid bacteria.J Dairy Sci. 2000 Dec;83(12):2740-6. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(00)75168-X. J Dairy Sci. 2000. PMID: 11132840
-
Sulfur metabolism in bacteria associated with cheese.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1999 Jul-Nov;76(1-4):247-61. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1999. PMID: 10532382 Review.
-
Methionine metabolism: major pathways and enzymes involved and strategies for control and diversification of volatile sulfur compounds in cheese.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2013;53(4):366-85. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2010.536918. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23320908 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae to release 3-Mercaptohexan-1-ol during fermentation through overexpression of an S. cerevisiae Gene, STR3, for improvement of wine aroma.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Jun;77(11):3626-32. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03009-10. Epub 2011 Apr 8. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21478306 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and characterization of two Lactobacillus casei genes encoding a cystathionine lyase.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Jan;74(1):99-106. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00745-07. Epub 2007 Nov 9. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 17993563 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous production of methionine-gamma-lyase from Brevibacterium linens in Lactococcus lactis and formation of volatile sulfur compounds.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Apr;75(8):2326-32. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02417-08. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19251895 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics of enzymes in flavor-forming pathways from amino acids in lactic acid bacteria.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Aug;74(15):4590-600. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00150-08. Epub 2008 Jun 6. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18539796 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Bacterium Hafnia alvei secretes l-methioninase enzyme: Optimization of the enzyme secretion conditions.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020 May;27(5):1222-1227. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.02.008. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32346328 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander, F. W., E. Sandmeier, P. K. Mehta, and P. Christen. 1994. Evolutionary relationships among pyridoxal-5′-phosphate-dependent enzymes. Regio-specific α, β, and γ families. Eur. J. Biochem. 219:953-960. - PubMed
-
- Aubel, D., J. E. Germond, C. Gilbert, and D. Atlan. 2002. Isolation of the patC gene encoding the cystathionine β-lyase of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and molecular analysis of inter-strain variability in enzyme biosynthesis. Microbiology 148:2029-2036. - PubMed
-
- Auger, S., M. P. Gomez, A. Danchin, and I. Martin-Verstraete. 2005. The PatB protein of Bacillus subtilis is a C-S-lyase. Biochimie 87:231-238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

