Ribosome binding to and dissociation from translocation sites of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane
- PMID: 16822833
- PMCID: PMC1593163
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-05-0439
Ribosome binding to and dissociation from translocation sites of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Abstract
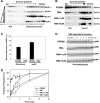
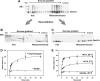
We have addressed how ribosome-nascent chain complexes (RNCs), associated with the signal recognition particle (SRP), can be targeted to Sec61 translocation channels of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane when all binding sites are occupied by nontranslating ribosomes. These competing ribosomes are known to be bound with high affinity to tetramers of the Sec61 complex. We found that the membrane binding of RNC-SRP complexes does not require or cause the dissociation of prebound nontranslating ribosomes, a process that is extremely slow. SRP and its receptor target RNCs to a free population of Sec61 complex, which associates with nontranslating ribosomes only weakly and is conformationally different from the population of ribosome-bound Sec61 complex. Taking into account recent structural data, we propose a model in which SRP and its receptor target RNCs to a Sec61 subpopulation of monomeric or dimeric state. This could explain how RNC-SRP complexes can overcome the competition by nontranslating ribosomes.
Figures



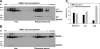

Similar articles
-
Binding of signal recognition particle gives ribosome/nascent chain complexes a competitive advantage in endoplasmic reticulum membrane interaction.Mol Biol Cell. 1998 Jan;9(1):103-15. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.1.103. Mol Biol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9436994 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Sec61alpha in the regulated transfer of the ribosome-nascent chain complex from the signal recognition particle to the translocation channel.Cell. 2000 Feb 4;100(3):333-43. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80669-8. Cell. 2000. PMID: 10676815
-
The intrinsic ability of ribosomes to bind to endoplasmic reticulum membranes is regulated by signal recognition particle and nascent-polypeptide-associated complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Oct 10;92(21):9435-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.21.9435. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7568149 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, function and evolution of the signal recognition particle.EMBO J. 2003 Jul 15;22(14):3479-85. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg337. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12853463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ribosome exchange revisited: a mechanism for translation-coupled ribosome detachment from the ER membrane.Trends Cell Biol. 2001 Mar;11(3):112-5. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)01905-x. Trends Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11306271 Review.
Cited by
-
Visualization of distinct entities of the SecYEG translocon during translocation and integration of bacterial proteins.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Mar;20(6):1804-15. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-08-0886. Epub 2009 Jan 21. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19158385 Free PMC article.
-
SRP keeps polypeptides translocation-competent by slowing translation to match limiting ER-targeting sites.Cell. 2008 May 2;133(3):440-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.049. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18455985 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome distribution in HeLa cells during the cell cycle.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32820. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032820. Epub 2012 Mar 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22403714 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian SRP receptor switches the Sec61 translocase from Sec62 to SRP-dependent translocation.Nat Commun. 2015 Dec 4;6:10133. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10133. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26634806 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial protein translocation requires only one copy of the SecY complex in vivo.J Cell Biol. 2012 Sep 3;198(5):881-93. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201205140. Epub 2012 Aug 27. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22927464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barle H., Essen P., Nyberg B., Olivecrona H., Tally M., McNurlan M. A., Wernerman J., Garlick P. J. Depression of liver protein synthesis during surgery is prevented by growth hormone. Am. J. Physiol. 1999;276:E620–E627. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann R., Spahn C. M., Eswar N., Helmers J., Penczek P. A., Sali A., Frank J., Blobel G. Architecture of the protein-conducting channel associated with the translating 80S ribosome. Cell. 2001;107:361–372. - PubMed
-
- Blobel G. Extraction from free ribosomes of a factor mediating ribosome detachment from rough microsomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1976;68:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

