BH3-only proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members Noxa and Puma mediate neural precursor cell death
- PMID: 16822983
- PMCID: PMC6673947
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0196-06.2006
BH3-only proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members Noxa and Puma mediate neural precursor cell death
Abstract
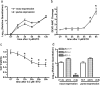
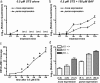
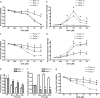
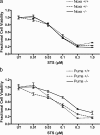
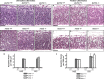
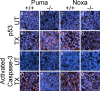
Neural precursor cells (NPCs) are highly sensitive to genotoxic injury, which triggers activation of the intrinsic mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway. This pathway is typically initiated by members of the BH3 (Bcl-2 homology 3)-only subgroup of the Bcl-2 (B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2) protein family, which are positioned upstream in the apoptotic pathway to respond to specific death stimuli. We have shown previously that NPCs deficient in the tumor suppressor protein p53 show significantly less death after exposure to genotoxic injury or to staurosporine (STS), a broad kinase inhibitor and potent apoptosis inducer. p53 has been shown to regulate the expression of both Noxa and Puma, two BH3-only proteins, although their involvement in p53-dependent cell death appears to be cell-type and stimulus specific. A systematic comparison of the relative contributions of Noxa and Puma to NPC apoptosis has not yet been performed. We hypothesized that p53-dependent transcription of Noxa and Puma leads to death in telencephalic NPCs exposed to genotoxic stress. We found that genotoxic injury induces a rapid p53-dependent increase in expression of Noxa and Puma mRNA in telencephalic NPCs. Furthermore, deficiency of either Noxa or Puma inhibited DNA damage-induced caspase-3 activation and cell death in telencephalic NPCs in vitro. However, only Puma deficiency protected telencephalic ventricular zone NPCs from death in vivo. In contrast to genotoxic injury, STS produced a p53-independent increase in Noxa and Puma expression, but neither Noxa nor Puma was required for STS-induced NPC death. Together, these experiments identify Noxa and Puma as important regulators of genotoxin-induced telencephalic NPC death.
Figures
References
-
- Akhtar RS, Roth KA (2006). Regulation of neural stem cell death. In: Neural development and stem cells (Rao MS, ed.) pp. 97–122. Totowa, NJ: Humana.
-
- Akhtar RS, Ness JM, Roth KA (2004). Bcl-2 family regulation of neuronal development and neurodegeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta 1644:189–203. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar RS, Geng Y, Klocke BJ, Roth KA (2006). Neural precursor cells possess multiple p53-dependent apoptotic pathways. Cell Death Differ in press. - PubMed
-
- Bounhar Y, Tounekti O, LeBlanc AC (2002). Monitoring caspases in neuronal cell death. In: Apoptosis techniques and protocols (LeBlanc AC, ed.) pp. 35–59. Totowa, NJ: Humana.
-
- Burger RM (1998). Cleavage of nucleic acids by bleomycin. Chem Rev 98:1153–1169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
