Crystal structures of saposins A and C
- PMID: 16823039
- PMCID: PMC2242594
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.062256606
Crystal structures of saposins A and C
Abstract
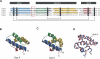
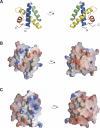
Saposins A and C are sphingolipid activator proteins required for the lysosomal breakdown of galactosylceramide and glucosylceramide, respectively. The saposins interact with lipids, leading to an enhanced accessibility of the lipid headgroups to their cognate hydrolases. We have determined the crystal structures of human saposins A and C to 2.0 Angstroms and 2.4 Angstroms, respectively, and both reveal the compact, monomeric saposin fold. We confirmed that these two proteins were monomeric in solution at pH 7.0 by analytical centrifugation. However, at pH 4.8, in the presence of the detergent C(8)E(5), saposin A assembled into dimers, while saposin C formed trimers. Saposin B was dimeric under all conditions tested. The self-association of the saposins is likely to be relevant to how these small proteins interact with lipids, membranes, and hydrolase enzymes.
Figures


References
-
- Abriouel H., Valdivia E., Galvez A., Maqueda M. 2001. Influence of physico-chemical factors on the oligomerization and biological activity of bacteriocin AS-48. Curr. Microbiol. 42: 89–95. - PubMed
-
- Ahn V.E., Faull K.F., Whitelegge J.P., Higginson J., Fluharty A.L., Privé G.G. 2003b. Expression, purification, crystallization, and preliminary X-ray analysis of recombinant human saposin B. Protein Expr. Purif. 27: 186–193. - PubMed
-
- Anderson D.H., Sawaya M.R., Cascio D., Ernst W., Modlin R., Krensky A., Eisenberg D. 2003. Granulysin crystal structure and a structure-derived lytic mechanism. J. Mol. Biol. 325: 355–365. - PubMed
-
- Azuma N., O'Brien J.S., Moser H.W., Kishimoto Y. 1994. Stimulation of acid ceramidase activity by saposin D. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 311: 354–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

