Neuregulin 1-Beta cytoprotective role in AML 12 mouse hepatocytes exposed to pentachlorophenol
- PMID: 16823072
- PMCID: PMC3785675
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph2006030002
Neuregulin 1-Beta cytoprotective role in AML 12 mouse hepatocytes exposed to pentachlorophenol
Abstract
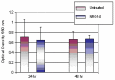
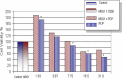
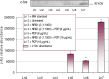
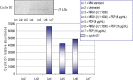
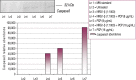
Neuregulins are a family of growth factor domain proteins that are structurally related to the epidermal growth factor. Accumulating evidence has shown that neuregulins have cyto- and neuroprotective properties in various cell types. In particular, the neuregulin-1 Beta (NRG1-Beta) isoform is well documented for its antiinflammatory properties in rat brain after acute stroke episodes. Pentachlorophenol (PCP) is an organochlorine compound that has been widely used as a biocide in several industrial, agricultural, and domestic applications. Previous investigations from our laboratory have demonstrated that PCP exerts both cytotoxic and mitogenic effects in human liver carcinoma (HepG2) cells, primary catfish hepatocytes and AML 12 mouse hepatocytes. We have also shown that in HepG2 cells, PCP has the ability to induce stress genes that may play a role in the molecular events leading to toxicity and tumorigenesis. In the present study, we hypothesize that NRG1-Beta will exert its cytoprotective effects in PCP-treated AML 12 mouse hepatocytes by its ability to suppress the toxic effects of PCP. To test this hypothesis, we performed the MTT-cell respiration assay to assess cell viability, and Western-blot analysis to assess stress-related proteins as a consequence of PCP exposure. Data obtained from 48 h-viability studies demonstrated a biphasic response; showing a dose-dependent increase in cell viability within the range of 0 to 3.87 microg/mL, and a gradual decrease within the concentration range of 7.75 to 31.0 microg/mL in concomitant treatments of NRG1-Beta+PCP and PCP. Cell viability percentages indicated that NRG1-Beta+PCPtreated cells were not significantly impaired, while PCP-treated cells were appreciably affected; suggesting that NRG1-Beta has the ability to suppress the toxic effects of PCP. Western Blot analysis demonstrated the potential of PCP to induce oxidative stress and inflammatory response (c-fos), growth arrest and DNA damage (GADD153), proteotoxic effects (HSP70), cell cycle arrest as consequence of DNA damage (p53), mitogenic response (cyclin- D1), and apoptosis (caspase-3). NRG1-Beta exposure attenuated stress-related protein expression in PCP-treated AML 12 mouse hepatocytes. Here we provide clear evidence that NRG1-Beta exerts cytoprotective effects in AML 12 mouse hepatocytes exposed to PCP.
Figures



References
-
- Crovello CS, Lai C, Cantley LC, Carraway KL., III Differential signaling by the epidermal growth factor-like growth factors neuregulin-1 and neuregulin -2. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:26954–26961. - PubMed
-
- Burden S, Yarden Y. Neuregulins and their receptors: a versatile signaling module in organogenesis and oncogenesis. Neuron. 1997;18:847–855. - PubMed
-
- Nakano N, Higashiyama S, Ohmoto H, Ishiguro H, Taniguchi N, Wada Y. The N-terminal region of NTAK/neuregulin-2 isoforms has an inhibitory activity on angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(12):11465–11470. - PubMed
-
- Parkinson DB, Langner K, Namini SS, Jessen KR, Mirksy R. β-Neuregulin and autocrine mediated survival of Schwann cells requires activity of Ets family transcription factors. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience. 2002;20:154–167. - PubMed
-
- Murphy S, Krainock R, Tham M. Neuregulin signaling via ErbB receptor assemblies in the nervous system. Molecular Neurobiology. 2002;25:67–78. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
