Inflammation and insulin resistance
- PMID: 16823477
- PMCID: PMC1483173
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI29069
Inflammation and insulin resistance
Erratum in
- J Clin Invest. 2006 Aug;116(8):2308
Abstract
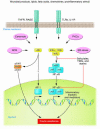
Over a hundred years ago, high doses of salicylates were shown to lower glucose levels in diabetic patients. This should have been an important clue to link inflammation to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes (T2D), but the antihyperglycemic and antiinflammatory effects of salicylates were not connected to the pathogenesis of insulin resistance until recently. Together with the discovery of an important role for tissue macrophages, these new findings are helping to reshape thinking about how obesity increases the risk for developing T2D and the metabolic syndrome. The evolving concept of insulin resistance and T2D as having immunological components and an improving picture of how inflammation modulates metabolism provide new opportunities for using antiinflammatory strategies to correct the metabolic consequences of excess adiposity.
Figures


References
-
- Ebstein W. Zur therapie des Diabetes mellitus, insbesondere über die Anwendung des salicylsauren Natron bei demselben. Berliner Klinische Wochenschrift. 1876;13:337–340.
-
- Shoelson S. Invited comment on W. Ebstein: on the therapy of diabetes mellitus, in particular on the application of sodium salicylate. J. Mol. Med. 2002;80:618–619. - PubMed
-
- Hecht A., Goldner M.G. Reappraisal of the hypoglycemic action of acetylsalicylate. Metabolism. 1959;8:418–428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

