Islet beta cell failure in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 16823478
- PMCID: PMC1483155
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI29103
Islet beta cell failure in type 2 diabetes
Abstract
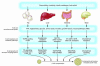
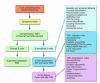
The major focus of this Review is on the mechanisms of islet beta cell failure in the pathogenesis of obesity-associated type 2 diabetes (T2D). As this demise occurs within the context of beta cell compensation for insulin resistance, consideration is also given to the mechanisms involved in the compensation process, including mechanisms for expansion of beta cell mass and for enhanced beta cell performance. The importance of genetic, intrauterine, and environmental factors in the determination of "susceptible" islets and overall risk for T2D is reviewed. The likely mechanisms of beta cell failure are discussed within the two broad categories: those with initiation and those with progression roles.
Figures

References
-
- Zimmet P., Alberti K.G., Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001;414:782–787. - PubMed
-
- Martin B.C., et al. Role of glucose and insulin resistance in development of type 2 diabetes mellitus: results of a 25-year follow-up study. Lancet. 1992;340:925–929. - PubMed
-
- Porte D. Clinical importance of insulin secretion and its interaction with insulin resistance in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2001;17:181–188. - PubMed
-
- Prentki M., Joly E., El-Assaad W., Roduit R. Malonyl-CoA signaling, lipid partitioning, and glucolipotoxicity: role in beta-cell adaptation and failure in the etiology of diabetes. Diabetes. 2002;51(Suppl. 3):S405–S413. - PubMed
-
- Leahy J.L. Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Med. Res. 2005;36:197–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

