Possible axonal regrowth in late recovery from the minimally conscious state
- PMID: 16823492
- PMCID: PMC1483160
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI27021
Possible axonal regrowth in late recovery from the minimally conscious state
Abstract
We used diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to study 2 patients with traumatic brain injury. The first patient recovered reliable expressive language after 19 years in a minimally conscious state (MCS); the second had remained in MCS for 6 years. Comparison of white matter integrity in the patients and 20 normal subjects using histograms of apparent diffusion constants and diffusion anisotropy identified widespread altered diffusivity and decreased anisotropy in the damaged white matter. These findings remained unchanged over an 18-month interval between 2 studies in the first patient. In addition, in this patient, we identified large, bilateral regions of posterior white matter with significantly increased anisotropy that reduced over 18 months. In contrast, notable increases in anisotropy within the midline cerebellar white matter in the second study correlated with marked clinical improvements in motor functions. This finding was further correlated with an increase in resting metabolism measured by PET in this subregion. Aberrant white matter structures were evident in the second patient's DTI images but were not clinically correlated. We propose that axonal regrowth may underlie these findings and provide a biological mechanism for late recovery. Our results are discussed in the context of recent experimental studies that support this inference.
Figures
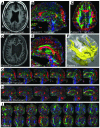

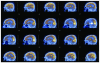
Comment in
-
Tracking the recovery of consciousness from coma.J Clin Invest. 2006 Jul;116(7):1823-5. doi: 10.1172/JCI29172. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 16823480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giacino J.T., et al. The minimally conscious state – definition and diagnostic criteria. Neurology. 2002;58:349–353. - PubMed
-
- Fins J.J. Constructing an ethical stereotaxy for severe brain injury: balancing risks, benefits and access. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003;4:323–327. - PubMed
-
- Basser P.J., Mattiello J., Le Bihan D.1994Estimation of the effective self–diffusion tensor from the NMR spin echo . J. Magn. Res. B. 103247–254. - PubMed
-
- Wakana S., Jiang H., Nagae-Poetscher L.M., van Zijl P.C., Mori S.2004Fiber tract–based atlas of human white matter anatomy . Radiology. 23077–87. - PubMed

