Loss of both Holliday junction processing pathways is synthetically lethal in the presence of gonococcal pilin antigenic variation
- PMID: 16824104
- PMCID: PMC2612780
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05213.x
Loss of both Holliday junction processing pathways is synthetically lethal in the presence of gonococcal pilin antigenic variation
Abstract
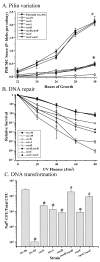
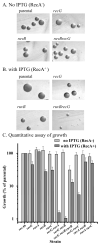
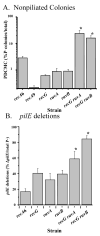
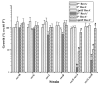
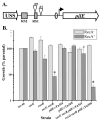
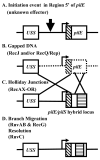
The obligate human pathogen Neisseria gonorrhoeae (Gc) has co-opted conserved recombination pathways to achieve immune evasion by way of antigenic variation (Av). We show that both the RuvABC and RecG Holliday junction (HJ) processing pathways are required for recombinational repair, each can act during genetic transfer, and both are required for pilin Av. Analysis of double mutants shows that either the RecG or RuvAB HJ processing pathway must be functional for normal growth of Gc when RecA is expressed. HJ processing-deficient survivors of RecA expression are enriched for non-piliated bacteria that carry large deletions of the pilE gene. Mutations that prevent pilin variation such as recO, recQ, and a cis-acting pilE transposon insertion all rescue the RecA-dependent growth inhibition of a HJ processing-deficient strain. These results show that pilin Av produces a recombination intermediate that must be processed by either one of the HJ pathways to retain viability, but requires both HJ processing pathways to yield pilin variants. The need for diversity generation through frequent recombination reactions creates a situation where the HJ processing machinery is essential for growth and presents a possible target for novel antimicrobials against gonorrhoea.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A genetic screen identifies genes and sites involved in pilin antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Jul;57(2):468-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04657.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15978078
-
Pilin antigenic variation occurs independently of the RecBCD pathway in Neisseria gonorrhoeae.J Bacteriol. 2009 Sep;191(18):5613-21. doi: 10.1128/JB.00535-09. Epub 2009 Jul 10. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19592592 Free PMC article.
-
RecQ DNA helicase HRDC domains are critical determinants in Neisseria gonorrhoeae pilin antigenic variation and DNA repair.Mol Microbiol. 2009 Jan;71(1):158-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06513.x. Epub 2008 Nov 11. Mol Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19017267 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation competence and type-4 pilus biogenesis in Neisseria gonorrhoeae--a review.Gene. 1997 Jun 11;192(1):125-34. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(97)00038-3. Gene. 1997. PMID: 9224882 Review.
-
Pilin gene variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: reassessing the old paradigms.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009 May;33(3):521-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00171.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19396954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Neisseria gonorrhoeae photolyase orthologue phrB is required for proper DNA supercoiling but does not function in photo-reactivation.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Feb;79(3):729-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07481.x. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21255115 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Pilin Antigenic Variation in Neisseria meningitidis by Next-Generation Sequencing.J Bacteriol. 2018 Oct 23;200(22):e00465-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00465-18. Print 2018 Nov 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 30181126 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of branch migration translocases with the Holliday junction-resolving enzyme and their implications in Holliday junction resolution.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jun 20;289(25):17634-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.552794. Epub 2014 Apr 25. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24770420 Free PMC article.
-
Suggested role for G4 DNA in recombinational switching at the antigenic variation locus of the Lyme disease spirochete.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57792. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057792. Epub 2013 Feb 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23469068 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the operon encoding the Holliday junction helicase RuvAB from Mycoplasma genitalium and its role in mgpB and mgpC gene variation.J Bacteriol. 2014 Apr;196(8):1608-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.01385-13. Epub 2014 Feb 14. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24532771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howell-Adams B, Seifert HS. Molecular models accounting for the gene conversion reactions mediating gonococcal pilin antigenic variation. Mol Microbiol. 2000;37:1146–1159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

