Tgfbr2 regulates the maintenance of boundaries in the axial skeleton
- PMID: 16824508
- PMCID: PMC1800905
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.06.002
Tgfbr2 regulates the maintenance of boundaries in the axial skeleton
Abstract
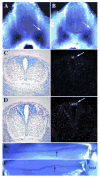
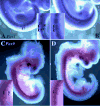
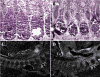
Previously, we showed that deletion of the TGF-beta type II receptor (Tgfbr2) in Type II Collagen (Col2a) expressing cells results in defects in the development of the axial skeleton. Defects included a reduction in size and alterations in the shape of specific vertebral elements. Anterior lateral and dorsal elements of the vertebrae were missing or irregularly shaped. Vertebral bodies were only mildly affected, but the intervertebral disc (IVD) was reduced or missing. In this manuscript, we show that alterations in the initiation or proliferation of cartilage are not detected in the axial skeleton. However, the expression domain of Fibromodulin (Fmod), a marker of the IVD, was reduced and the area of the future IVD contained peanut agglutinin (PNA) staining cartilage. Next, we show that the expression domains of Pax1 and Pax9, which are preferentially expressed in the caudal sclerotome, are expanded over the entire rostral to caudal length of the sclerotome segment. Dorsal-ventral patterning was not affected in these mice as accessed by expression of Pax1, Pax9, and Msx1. Proliferation was modestly reduced in the loose cells of the sclerotome. The results suggest that signaling through Tgfbr2 regulates the maintenance of boundaries in the sclerotome and developing axial skeleton.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conditional deletion of the TGF-beta type II receptor in Col2a expressing cells results in defects in the axial skeleton without alterations in chondrocyte differentiation or embryonic development of long bones.Dev Biol. 2004 Dec 1;276(1):124-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.08.027. Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15531369
-
Molecular profiling of the developing mouse axial skeleton: a role for Tgfbr2 in the development of the intervertebral disc.BMC Dev Biol. 2010 Mar 9;10:29. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-10-29. BMC Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20214815 Free PMC article.
-
PDGF mediates TGFβ-induced migration during development of the spinous process.Dev Biol. 2012 May 1;365(1):110-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.02.013. Epub 2012 Feb 18. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22369999 Free PMC article.
-
The development of the avian vertebral column.Anat Embryol (Berl). 2000 Sep;202(3):179-94. doi: 10.1007/s004290000114. Anat Embryol (Berl). 2000. PMID: 10994991 Review.
-
No major contribution of the TGFBR1- and TGFBR2-mediated pathway to Kabuki syndrome.Am J Med Genet A. 2006 Apr 15;140(8):903-5. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31168. Am J Med Genet A. 2006. PMID: 16528739 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Intervertebral disc development and disease-related genetic polymorphisms.Genes Dis. 2016 Apr 23;3(3):171-177. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2016.04.006. eCollection 2016 Sep. Genes Dis. 2016. PMID: 30258887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inactivation of FAM20B causes cell fate changes in annulus fibrosus of mouse intervertebral disc and disc defects via the alterations of TGF-β and MAPK signaling pathways.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019 Dec 1;1865(12):165555. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.165555. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019. PMID: 31513834 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of fucosyltransferase 8 reverses the inhibitory effect of high-dose dexamethasone on osteogenic response of MC3T3-E1 preosteoblasts.PeerJ. 2021 Dec 9;9:e12380. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12380. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34966572 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonism of BMP signaling is insufficient to induce fibrous differentiation in primary sclerotome.Exp Cell Res. 2019 May 1;378(1):11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.01.026. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Exp Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 30817928 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Smad4 in the scleraxis cell lineage results in postnatal joint contracture.Dev Biol. 2021 Feb;470:108-120. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.11.006. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33248111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baffi MO, Slattery E, Sohn P, Moses HL, Chytil A, Serra R. Conditional deletion of the TGF-beta type II receptor in Col2a expressing cells results in defects in the axial skeleton without alterations in chondrocyte differentiation or embryonic development of long bones. Dev Biol. 2004;276:124–142. - PubMed
-
- Bagnall KM, Sanders EJ. The binding pattern of peanut lectin associated with sclerotome migration and the formation of the vertebral axis in the chick embryo. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1989;180:505–513. - PubMed
-
- Bagnall KM, Sanders EJ, Berdan RC. Communication compartments in the axial mesoderm of the chick embryo. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1992;186:195–204. - PubMed
-
- Balling R, Helwig U, Nadeau J, Neubuser A, Schmahl W, Imai K. Pax genes and skeletal development. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996;785:27–33. - PubMed
-
- Bronner-Fraser M. Mechanisms of neural crest cell migration. BioEssays. 1993;15:221–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

