Suppression of hippocampal plasticity-related gene expression by sleep deprivation in rats
- PMID: 16825295
- PMCID: PMC1995680
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.115287
Suppression of hippocampal plasticity-related gene expression by sleep deprivation in rats
Abstract
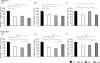
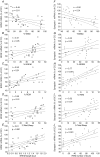
Previous work shows that sleep deprivation impairs hippocampal-dependent learning and long-term potentiation (LTP). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), cAMP response-element-binding (CREB) and calcium-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CAMKII) are critical modulators of hippocampal-dependent learning and LTP. In the present study we compared the effects of short- (8 h) and intermediate-term (48 h) sleep deprivation (SD) on the expression of BDNF and its downstream targets, Synapsin I, CREB and CAMKII in the neocortex and the hippocampus. Rats were sleep deprived using an intermittent treadmill system which equated total movement in the SD and control treadmill animals (CT), but permitted sustained periods of rest in CT animals. Animals were divided into SD (treadmill schedule: 3 s on/12 s off) and two treadmill control groups, CT1 (15 min on/60 min off) and CT2 (30 min on/120 min off - permitting more sustained sleep). Real-time Taqman RT-PCR was used to measure changes in mRNA; BDNF protein levels were determined using ELISA. In the hippocampus, 8 h treatments reduced BDNF, Synapsin I, CREB and CAMKII gene expression in both SD and control groups. Following 48 h of experimental procedures, the expression of all these four molecular markers of plasticity was reduced in SD and CT1 groups compared to the CT2 and cage control groups. In the hippocampus, BDNF protein levels after 8 h and 48 h treatments paralleled the changes in mRNA. In neocortex, neither 8 h nor 48 h SD or control treatments had significant effects on BDNF, Synapsin I and CAMKII mRNA levels. Stepwise regression analysis suggested that loss of REM sleep underlies the effects of SD on hippocampal BDNF, Synapsin I and CREB mRNA levels, whereas loss of NREM sleep underlies the effects on CAMKII mRNA.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Melatonin ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by sleep deprivation in rats: role of oxidative stress, BDNF and CaMKII.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Nov 1;256:72-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.07.051. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23933144
-
Differential gene expression in the rat hippocampus during learning of an operant conditioning task.Neuroscience. 2009 Nov 10;163(4):1031-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.07.037. Epub 2009 Jul 24. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19632308
-
Effects of post-learning REM sleep deprivation on hippocampal plasticity-related genes and microRNA in mice.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Apr 1;361:7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.12.045. Epub 2018 Dec 27. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30594545
-
BDNF-induced local protein synthesis and synaptic plasticity.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:639-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23602987 Review.
-
BDNF mechanisms in late LTP formation: A synthesis and breakdown.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:664-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.06.024. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23831365 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of chronic moderate sleep restriction and exercise training on anxiety, spatial memory, and associated neurobiological measures in mice.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Aug 1;250:74-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.04.038. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23644185 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tinospora cordifolia ameliorates anxiety-like behavior and improves cognitive functions in acute sleep deprived rats.Sci Rep. 2016 May 5;6:25564. doi: 10.1038/srep25564. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27146164 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic analysis of sleep deprivation reveals translational regulation in the hippocampus.Physiol Genomics. 2012 Oct 17;44(20):981-91. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00084.2012. Epub 2012 Aug 28. Physiol Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22930738 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep oscillations in the thalamocortical system induce long-term neuronal plasticity.Neuron. 2012 Sep 20;75(6):1105-13. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.08.034. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 22998877 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating role of serotonergic signaling in sleep and memory.Pharmacol Rep. 2022 Feb;74(1):1-26. doi: 10.1007/s43440-021-00339-8. Epub 2021 Nov 6. Pharmacol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34743316 Review.
References
-
- Alsina B, Vu T, Cohen-Cory S. Visualizing synapse formation in arborizing optic axons in vivo: dynamics and modulation by BDNF. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:1093–1101. - PubMed
-
- Barde YA. Neurotrophins: a family of proteins supporting the survival of neurons. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1994;390:45–56. - PubMed
-
- Benington JH, Frank MG. Cellular and molecular connections between sleep and synaptic plasticity. Prog Neurobiol. 2003;69:71–101. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet MH, Arand DL. Clinical effects of sleep fragmentation versus sleep deprivation. Sleep Med Rev. 2003;7:297–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

