Molecular typing reveals a unique clone of Salmonella enterica serotype typhi among Indian strains
- PMID: 16825414
- PMCID: PMC1489529
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02514-05
Molecular typing reveals a unique clone of Salmonella enterica serotype typhi among Indian strains
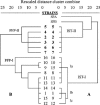
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular typing of Salmonella enterica serovar typhi.J Clin Microbiol. 1996 Nov;34(11):2831-4. doi: 10.1128/jcm.34.11.2831-2834.1996. J Clin Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8897193 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemic typhoid in Chile: analysis by molecular and conventional methods of Salmonella typhi strain diversity in epidemic (1977 and 1981) and nonepidemic (1990) years.J Clin Microbiol. 1996 Jul;34(7):1701-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.34.7.1701-1707.1996. J Clin Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8784573 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi in Dakar, Senegal.Clin Infect Dis. 2003 Aug 1;37(3):465-6. doi: 10.1086/376646. Clin Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12884182 No abstract available.
-
[The molecular epidemiology of typhoid].Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1996 Jul-Aug;(4):96-9. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1996. PMID: 9027187 Review. Russian. No abstract available.
-
Navigating the future of bacterial molecular epidemiology.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010 Oct;13(5):640-5. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2010.08.002. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20846899 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chaudhry, R., R. K. Mahajan, A. Diwan, S. Khan, R. Singhal, D. S. Chandel, and C. Hans. 2003. Unusual presentation of enteric fever: three cases of splenic and liver abscesses due to Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi A. Trop. Gastroenterol. 24:198-199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

