Girls' activity levels and lesson contexts in middle school PE: TAAG baseline
- PMID: 16826019
- PMCID: PMC2431981
- DOI: 10.1249/01.mss.0000227307.34149.f3
Girls' activity levels and lesson contexts in middle school PE: TAAG baseline
Abstract
Purpose: To assess girls' physical activity (PA) in middle school physical education (PE) as it relates to field site, lesson context and location, teacher gender, and class composition.
Methods: We observed girls' PA levels, lesson contexts, and activity promotion by teachers in 431 lessons in 36 schools from six field sites participating in the Trial of Activity for Adolescent Girls. Interobserver reliabilities exceeded 90% for all three categories. Data were analyzed using mixed-model ANOVA with controls for clustering effects by field site and school.
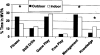
Results: Mean lesson length was 37.3 (+/-9.4) min. Time (13.9+/-7.0 min) and proportion of lessons (37.9+/-18.5%) spent in moderate to vigorous PA (MVPA), and time (4.8+/-4.2 min) and proportion of lessons (13.1+/-11.7%) in vigorous PA (VPA) differed by field site (P<0.004). Lesson time for instructional contexts differed by field site, with overall proportions as follows: game play (27.3%), management (26.1%), fitness activities (19.7%), skill drills (12.1%), knowledge (10.6%), and free play (4.4%). Coed classes were 7.9 min longer than girls-only classes (P=0.03). Although 27 s shorter, outdoor lessons were more intense (MVPA%=45.7 vs 33.7% of lesson, P<0.001) and provided 4.0 more MVPA minutes (P<0.001). MVPA, VPA, and lesson contexts did not differ by teacher gender. There was little direct promotion of PA by teachers during lessons.
Conclusions: Substantial variation in the conduct of PE exists. Proportion of lesson time girls spent accruing MVPA (i.e., 37.9%) fell short of the Healthy People 2010 objective of 50%. Numerous possibilities exist for improving girls' PA in PE.
Figures


References
-
- Biddle S, Cavill N, Sallis J, Biddle S, Sallis J, Cavill N. Young and Active? Young People and Health-Enhancing Physical Activity: Evidence and Implications. Health Education Authority; London: 1998. Policy framework for young people and health-enhancing physical activity. pp. 3–16.
-
- Burgeson CR, Wechsler H, Brener N, Young J, Spain C. Physical education and activity: Results of the School Health Policies and Programs Study 2000. J. Sch. Health. 2001;71:279–293. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Conrol and Prevnton Guidelines for school and community programs to promote lifelong physical activity among young people. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 1997;46:1–35. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Promoting Better Health for Young People through Physical Activity and Sports: A Report to the President from the Secretary of Health and Human Services and the Secretary of Education. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Washington, DC: 2000. pp. 1–36.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Increasing physical activity: a report on recommendations on the Task Force on Community Preventive Services. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2001;50:1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UO1HL066858/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066855/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UO1HL066853/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UO1HL066857/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066858/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066857/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066845/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UO1HL066855/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066852/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066853/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UO1HL066852/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UO1HL066845/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UO1HL066856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States

