Inhibition of neuroblastoma xenograft growth by Hsp90 inhibitors
- PMID: 16827123
- PMCID: PMC2613690
Inhibition of neuroblastoma xenograft growth by Hsp90 inhibitors
Abstract
Background: Advanced-stage neuroblastomas are often resistant to chemotherapy. Heat shock protein (Hsp) 90 is a molecular chaperone that maintains the stability of important signal transduction proteins. We have previously reported that geldanamycin (GA), an Hsp90 inhibitor, decreases Raf-1 and Akt protein expressions and induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. We sought to determine the in vivo effects of Hsp90 inhibitor compounds on human neuroblastomas.
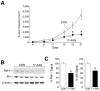
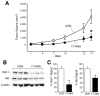
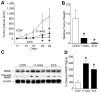
Materials and methods: Human neuroblastoma (LAN-1 and SK-N-SH) xenografts (4-mm3 tumor implants) were placed in the flanks of athymic nude mice. The mice received either Hsp90 inhibitors (17-AAG or EC5) or vehicle (control). The tumor dimensions were measured twice weekly. Proteins were extracted for Western immunoblotting.
Results: Hsp90 inhibitor compounds significantly blocked both LAN-1 and SK-N-SH neuroblastoma growth in vivo. Drug-treated tumors showed decreases in Raf-1 and cleaved PARP expressions.
Conclusion: Hsp90 inhibitors may prove to be important novel therapeutic agents for patients with advanced-stage neuroblastoma who fail to respond to current treatment regimens.
Figures
References
-
- Shimada H, Ambros IM, Dehner LP, Hata J, Joshi VV, Roald B. Terminology and morphologic criteria of neuroblastic tumors: recommendations by the International Neuroblastoma Pathology Committee. Cancer. 1999;86:349–363. - PubMed
-
- Teitz T, Lahti JM, Kidd VJ. Aggressive childhood neuroblastomas do not express caspase-8: an important component of programmed cell death. J Mol Med. 2001;79:428–436. - PubMed
-
- Neckers L, Ivy SP. Heat shock protein 90. Curr Opin Oncol. 2003;15:419–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
