Alternative tyrosine phosphorylation of signaling kinases according to hormone receptor status in breast cancer overexpressing the insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1
- PMID: 16827799
- PMCID: PMC11158992
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00228.x
Alternative tyrosine phosphorylation of signaling kinases according to hormone receptor status in breast cancer overexpressing the insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1
Abstract
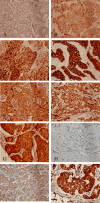
The insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1 (IGF1R) is suggested to play important roles in cancer cell growth through cross-talk with hormone receptors and growth factor receptors. However, its clinical significance in breast cancers in vivo is still unclear. We examined immunohistochemically the expression of IGF1R, phosphorylated-AKT (pAKT) and phosphorylated-ERK1/2 (pERK1/2) using tissue microarray slides containing 150 cases of primary breast carcinoma. Their mutual correlation and correlation with the status of hormone receptors epidermal growth factor receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 were also investigated. IGF1R overexpression was detected in 71 cases (47%), and was correlated with lower nuclear grade (P = 0.03), positive estrogen receptor (ER) and/or progesterone receptor status (P = 0.002). pERK1/2 expression, detected in 53 cases (35%), was correlated with positive ER (P < 0.0001) and lower nuclear grade (P = 0.014). pAKT expression, detected in 88 cases (59%), was not correlated with nuclear grade, hormone receptors status or other clinical parameters. Of the 71 IGF1R-overexpressing tumors, pERK1/2 expression was detected in 27 (56%) of 48 ER-positive cases but in only four (17%) of 23 ER-negative cases (P = 0.022). In contrast, pAKT expression was constantly (64% or higher) detected irrespective of hormone receptor status in IGF1R-overexpressing breast cancers. Taken together, these findings suggest that IGF1R overexpression might activate pERK1/2 and pAKT in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, but activate only pAKT in hormone receptor-negative breast cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic relevance of activated Akt kinase in node-negative breast cancer: a clinicopathological study of 99 cases.Mod Pathol. 2004 Jan;17(1):15-21. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800002. Mod Pathol. 2004. PMID: 14631376
-
Differential insulin-like growth factor I receptor signaling and function in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive MCF-7 and ER-negative MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2001 Sep 15;61(18):6747-54. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11559546
-
Determination of HER2 phosphorylation at tyrosine 1221/1222 improves prediction of poor survival for breast cancer patients with hormone receptor-positive tumors.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(1):R11. doi: 10.1186/bcr2230. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19239686 Free PMC article.
-
Mediator of ERBB2-driven cell motility (MEMO) promotes extranuclear estrogen receptor signaling involving the growth factor receptors IGF1R and ERBB2.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 23;288(34):24590-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.467837. Epub 2013 Jul 16. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23861392 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of erbB receptor (HER) tyrosine kinases as a strategy to abrogate antiestrogen resistance in human breast cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2001 Dec;7(12 Suppl):4436s-4442s; discussion 4411s-4412s. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11916237 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic impact of imaging of breast cancer angiogenesis and hypoxia using diffuse optical spectroscopy.Cancer Sci. 2014 Jul;105(7):833-9. doi: 10.1111/cas.12432. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Cancer Sci. 2014. PMID: 24766271 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine, by acting through its D2 receptor, inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I)-induced gastric cancer cell proliferation via up-regulation of Krüppel-like factor 4 through down-regulation of IGF-IR and AKT phosphorylation.Am J Pathol. 2010 Dec;177(6):2701-7. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100617. Epub 2010 Nov 12. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 21075859 Free PMC article.
-
Optical imaging of tumor vascularity associated with proliferation and glucose metabolism in early breast cancer: clinical application of total hemoglobin measurements in the breast.BMC Cancer. 2013 Oct 31;13:514. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-514. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24176197 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) tyrosine kinase as a novel cancer therapy approach.J Med Chem. 2009 Aug 27;52(16):4981-5004. doi: 10.1021/jm9002395. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19610618 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
The impact of IGF-1R expression on the outcomes of patients with breast cancer: a meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Jan 29;8:279-87. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S74774. eCollection 2015. Onco Targets Ther. 2015. PMID: 25674003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnston SR. Combinations of endocrine and biological agents: present status of therapeutic and presurgical investigations. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11 (2 Part 2): S889–99. - PubMed
-
- Geisler J, Lonning PE. Aromatase inhibition: translation into a successful therapeutic approach. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 2809–21. - PubMed
-
- Hayes DF, Thor AD. c‐erbB‐2 in breast cancer: development of a clinically useful marker. Semin Oncol 2002; 29: 231–45. - PubMed
-
- Revillion F, Bonneterre J, Peyrat JP. ERBB2 oncogene in human breast cancer and its clinical significance. Eur J Cancer 1998; 34: 791–808. - PubMed
-
- Walker RA, Dearing SJ. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor mRNA and protein in primary breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1999; 53: 167–76. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

