Plant cells recognize chitin fragments for defense signaling through a plasma membrane receptor
- PMID: 16829581
- PMCID: PMC1636686
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0508882103
Plant cells recognize chitin fragments for defense signaling through a plasma membrane receptor
Abstract
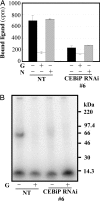
Chitin is a major component of fungal cell walls and serves as a molecular pattern for the recognition of potential pathogens in the innate immune systems of both plants and animals. In plants, chitin oligosaccharides have been known to induce various defense responses in a wide range of plant cells including both monocots and dicots. To clarify the molecular machinery involved in the perception and transduction of chitin oligosaccharide elicitor, a high-affinity binding protein for this elicitor was isolated from the plasma membrane of suspension-cultured rice cells. Characterization of the purified protein, CEBiP, as well as the cloning of the corresponding gene revealed that CEBiP is actually a glycoprotein consisting of 328 amino acid residues and glycan chains. CEBiP was predicted to have a short membrane spanning domain at the C terminus. Knockdown of CEBiP gene by RNA interference resulted in the suppression of the elicitor-induced oxidative burst as well as the gene responses, showing that CEBiP plays a key role in the perception and transduction of chitin oligosaccharide elicitor in the rice cells. Structural analysis of CEBiP also indicated the presence of two LysM motifs in the extracellular portion of CEBiP. As the LysM motif has been known to exist in the putative Nod-factor receptor kinases involved in the symbiotic signaling between leguminous plants and rhizobial bacteria, the result indicates the involvement of partially homologous plasma membrane proteins both in defense and symbiotic signaling in plant cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures





Comment in
-
LysM receptors recognize friend and foe.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jul 18;103(29):10829-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604601103. Epub 2006 Jul 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16832046 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Two LysM receptor molecules, CEBiP and OsCERK1, cooperatively regulate chitin elicitor signaling in rice.Plant J. 2010 Oct;64(2):204-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04324.x. Epub 2010 Sep 7. Plant J. 2010. PMID: 21070404 Free PMC article.
-
Chitin-induced activation of immune signaling by the rice receptor CEBiP relies on a unique sandwich-type dimerization.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 21;111(3):E404-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312099111. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24395781 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the chimeric receptor between the chitin elicitor receptor CEBiP and the receptor-like protein kinase Pi-d2 leads to enhanced responses to the chitin elicitor and disease resistance against Magnaporthe oryzae in rice.Plant Mol Biol. 2013 Feb;81(3):287-95. doi: 10.1007/s11103-012-9998-7. Epub 2012 Dec 16. Plant Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23242918
-
Defense Against Pathogens: Structural Insights into the Mechanism of Chitin Induced Activation of Innate Immunity.Curr Med Chem. 2017 Nov 24;24(36):3980-3986. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666161221124345. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28003004 Review.
-
Chitin-mediated plant-fungal interactions: catching, hiding and handshaking.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2015 Aug;26:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2015.05.032. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 26116978 Review.
Cited by
-
OsLYP4 and OsLYP6 play critical roles in rice defense signal transduction.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 Feb;8(2):e22980. doi: 10.4161/psb.22980. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23299421 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering plant immune circuit: walking to the bright future with a novel toolbox.Plant Biotechnol J. 2023 Jan;21(1):17-45. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13916. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Plant Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 36036862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma Membrane Microdomains Are Essential for Rac1-RbohB/H-Mediated Immunity in Rice.Plant Cell. 2016 Aug;28(8):1966-83. doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00201. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Plant Cell. 2016. PMID: 27465023 Free PMC article.
-
A haustorial-expressed lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase from the cucurbit powdery mildew pathogen Podosphaera xanthii contributes to the suppression of chitin-triggered immunity.Mol Plant Pathol. 2021 May;22(5):580-601. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13045. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Mol Plant Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33742545 Free PMC article.
-
The ubiquitin ligase PUB22 targets a subunit of the exocyst complex required for PAMP-triggered responses in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2012 Nov;24(11):4703-16. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.104463. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 23170036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boller T. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1995;46:189–214.
-
- Dangl J. L., Jones J. D. G. Nature. 2001;411:826–833. - PubMed
-
- Nürnberger T., Brunner F., Kemmerling B., Piater L. Immunol. Rev. 2004;198:249–266. - PubMed
-
- Shibuya N., Minami E. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2001;59:223–233.
-
- Furukawa S., Taniai K., Yang J., Shono T., Yamakawa M. Insect Mol. Biol. 1999;8:145–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

