Persisting immune responses indicating long-term protection after booster dose with meningococcal group B outer membrane vesicle vaccine
- PMID: 16829617
- PMCID: PMC1489568
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00047-06
Persisting immune responses indicating long-term protection after booster dose with meningococcal group B outer membrane vesicle vaccine
Abstract
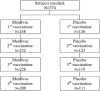
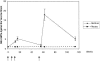
MenBvac is an outer membrane vesicle vaccine against systemic meningococcal disease caused by serogroup B Neisseria meningitidis. In this placebo-controlled double-blind study including 374 healthy adolescents, the safety and immunogenicity of a schedule of three primary doses 6 weeks apart followed by a fourth dose a year later were evaluated. Antibody responses to the vaccine strain and heterologous strains (non-vaccine-type strains) and the persistence of these antibodies were measured by the serum bactericidal assay (SBA) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay up to 1 year after the last dose. The proportion of subjects with SBA titers of > or = 4 against the vaccine strain increased from 3% prevaccination to 65% after the third dose. Ten months later, this proportion had declined to 28%. The fourth dose induced a booster response demonstrated by 93% of subjects achieving a titer of > or = 4. One year after the booster dose, 64% still showed SBA titers of > or = 4. Cross-reacting antibodies were induced against all heterologous strains tested, although the magnitude of SBA titers differed widely between the different strains. All four doses of MenBvac were safe. Both MenBvac and the placebo had reactogenicity profiles of mild to moderate local and systemic reactions. Pain, the most common reaction, was reported with similar frequencies in both groups. No serious adverse events occurred in the MenBvac group. This study confirmed the good immunogenicity of the primary course of MenBvac and demonstrated prolonged persistence and increased cross-reactivity of functional antibodies elicited by a booster dose.
Figures
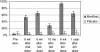
Similar articles
-
Immunogenicity and safety of a combination of two serogroup B meningococcal outer membrane vesicle vaccines.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007 Sep;14(9):1062-9. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00094-07. Epub 2007 Jul 18. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17634513 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison and correlation of neisseria meningitidis serogroup B immunologic assay results and human antibody responses following three doses of the Norwegian meningococcal outer membrane vesicle vaccine MenBvac.Infect Immun. 2006 Aug;74(8):4557-65. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00466-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16861642 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Combined administration of meningococcal serogroup B outer membrane vesicle vaccine and conjugated serogroup C vaccine indicated for prevention of meningococcal disease is safe and immunogenic.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2005 May;12(5):599-605. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.12.5.599-605.2005. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15879021 Free PMC article.
-
Multicomponent meningococcal serogroup B vaccine (4CMenB; Bexsero(®)): a review of its use in primary and booster vaccination.BioDrugs. 2013 Jun;27(3):263-74. doi: 10.1007/s40259-013-0029-2. BioDrugs. 2013. PMID: 23575646 Review.
-
Immunogenicity and safety of the multicomponent meningococcal B vaccine (4CMenB) in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Infect Dis. 2018 Apr;18(4):461-472. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30048-3. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29371070
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicles released by host epithelial cells during Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection function as homing beacons for neutrophils.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jun 21;22(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01609-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38907250 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity, reactogenicity, and safety of a P1.7b,4 strain-specific serogroup B meningococcal vaccine given to preteens.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007 Nov;14(11):1393-9. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00167-07. Epub 2007 Sep 26. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17898183 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Vaccination strategies for the prevention of meningococcal disease.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2018 May 4;14(5):1203-1215. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1451287. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2018. PMID: 29543535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular Immune Responses in Humans Induced by Two Serogroup B Meningococcal Outer Membrane Vesicle Vaccines Given Separately and in Combination.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2016 Apr 4;23(4):353-62. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00666-15. Print 2016 Apr. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26865595 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Modulate Corneal Inflammation: Role in Microbial Keratitis?Infect Immun. 2023 Apr 18;91(4):e0003623. doi: 10.1128/iai.00036-23. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Infect Immun. 2023. PMID: 36995231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aaberge, I. S., P. Oster, O. S. Helland, A.-C. Kristoffersen, E. Ypma, E. A. Høiby, B. Feiring, and H. Nøkleby. 2005. Combined administration of meningococcal serogroup B outer membrane vesicle vaccine and conjugated serogroup C vaccine indicated for prevention of meningococcal disease is safe and immunogenic. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 12:599-605. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker, M. G., D. R. Martin, C. E. Kieft, and D. Lennon. 2001. A 10-year serogroup B meningococcal disease epidemic in New Zealand: descriptive epidemiology, 1991-2000. J. Paediatr. Child Health 37:S13-S19. - PubMed
-
- Bjune, G., E. A. Høiby, J. K. Grønnesby, O. Arnesen, J. H. Fredriksen, A. Halstensen, E. Holten, A. K. Lindbak, H. Nøkleby, E. Rosenqvist, L. K. Solberg, O. Closs, J. Eng, L. Froholm, A. Lystad, L. Bakketein, and B. Hareide. 1991. Effect of outer membrane vesicle vaccine against group B meningococcal disease in Norway. Lancet 338:1093-1096. - PubMed
-
- Borrow, R., P. Balmer, and E. Miller. 2005. Meningococcal surrogates of protection-serum bactericidal antibody activity. Vaccine 23:2222-2227. - PubMed
-
- Borrow, R., I. S. Aaberge, G. F. Santos, T. L. Eudey, P. Oster, A. Glennie, J. Findlow, E. A. Høiby, E. Rosenqvist, P. Balmer, and D. Martin. 2005. Interlaboratory standardization of the measurement of serum bactericidal activity by using human complement against meningococcal serogroup B, strain 44/76-SL, before and after vaccination with the Norwegian MenBvac outer membrane vesicle vaccine. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 12:970-976. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

