Increasing minority research participation through community organization outreach
- PMID: 16829637
- PMCID: PMC2536763
- DOI: 10.1177/0193945906287215
Increasing minority research participation through community organization outreach
Abstract
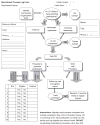
Recruitment is one of the most significant challenges in conducting research with ethnic minority populations. Establishing relationships with organizations that serve ethnic minority communities can facilitate recruitment. To create a successful recruitment process, a strategic plan of action is necessary prior to implementing community outreach efforts. For this study population of women who were HIV+ and recovering from substance abuse disorder, the authors found that establishing trust with community organizations that serve these women allows for a productive referral relationship. Although the majority of women in this study are African American, the authors were particularly challenged in recruiting Hispanic women. This article presents a recruitment process model that has facilitated our recruitment efforts and has helped the authors to organize, document, and evaluate their community out-reach strategies. This model can be adopted and adapted by nurses and other health researchers to enhance engagement of minority populations.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4. Washington, DC: Author; 1994.
-
- Atkinson R, Flint J. Accessing hidden and hard-to-reach populations: Snowball research strategies. Social Research Update, University of Surrey. 2001;33:1–4.
-
- Bailey JM, Bieniasz ME, Kmak D, Brenner DE, Ruffin MT. Recruitment and retention of economically underserved women to a cervical cancer prevention trial. Applied Nursing Research. 2004;17(1):55–60. - PubMed
-
- Benoit C, Jansson M, Millar A, Phillips R. Community-academic research on hard-to-reach populations: Benefits and challenges. Qualitative Health Research. 2005;15(2):263–282. - PubMed
-
- Brown DR, Fouad MN, Basen-Engquist K, Tortolero-Luna G. Recruitment and retention of minority women in cancer screening, prevention, and treatment trials. Annals of Epidemiology. 2000;10(S8):S13–S21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources