Amplification of chromosome 21q22.3 harboring trefoil factor family genes in liver fluke related cholangiocarcinoma is associated with poor prognosis
- PMID: 16830362
- PMCID: PMC4087361
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i26.4143
Amplification of chromosome 21q22.3 harboring trefoil factor family genes in liver fluke related cholangiocarcinoma is associated with poor prognosis
Abstract
Aim: To determine allelic imbalance on chromosomal region 21q22-qter including trefoil factor family genes (TFF) in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) patients and analyze the correlation between allelic imbalances and clinicopathological parameters.
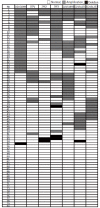
Methods: Quantitative PCR amplification was performed on four microsatellite markers and trefoil factor family genes (TFF1, TFF2, and TFF3) using a standard curve and SYBR Green I dye method. The relative copy number was determined by DNA copy number of tested locus to reference locus. The relative copy number was interpreted as deletion or amplification by comparison with normal reference range. Associations between allelic imbalance and clinicopathological parameters of CCA patients were evaluated by chi(2)-tests. Kaplan-Meier method was used to analyze survival.
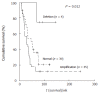
Results: The frequencies of amplification at D21S1890, D21S1893, and TFF3 were 32.5%, 30.0%, and 28.7%, respectively. Patients who had amplification at regions covering D21S1893, D21S1890, and TFF showed poor prognosis, whereas patients who had deletion showed favorable prognosis (mean: 51.7 wk vs 124.82 wk, P = 0.012). Multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that amplification of D21S1893, D21S1890 and TFF, blood vessel invasion, and staging were associated with poor prognosis.
Conclusion: D21S1893-D21S1890 region may harbor candidate genes especially TFF and serine protease family, which might be involved in tumor invasion and metastasis contributing to poor survival. The amplification in this region may be used as a prognostic marker in the treatment of CCA patients.
Figures
References
-
- Uttaravichien T, Bhudhisawasdi V, Pairojkul C, Pugkhem A. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in Thailand. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1999;6:128–135. - PubMed
-
- Nakanuma Y, Hoso M, Sanzen T, Sasaki M. Microstructure and development of the normal and pathologic biliary tract in humans, including blood supply. Microsc Res Tech. 1997;38:552–570. - PubMed
-
- Sriamporn S, Pisani P, Pipitgool V, Suwanrungruang K, Kamsa-ard S, Parkin DM. Prevalence of Opisthorchis viverrini infection and incidence of cholangiocarcinoma in Khon Kaen, Northeast Thailand. Trop Med Int Health. 2004;9:588–594. - PubMed
-
- Shaib Y, El-Serag HB. The epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2004;24:115–125. - PubMed
-
- Watanapa P, Watanapa WB. Liver fluke-associated cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Surg. 2002;89:962–970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

