Differential treatment and early outcome in the interventional endoscopic management of pancreatic pseudocysts in 27 patients
- PMID: 16830368
- PMCID: PMC4087367
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i26.4175
Differential treatment and early outcome in the interventional endoscopic management of pancreatic pseudocysts in 27 patients
Abstract
Aim: Pancreatic pseudocysts (PPC) as a complication of pancreatitis are approached only in the case of abdominal pain, infection, bleeding, and compression onto the gastrointestinal tract or biliary tree.
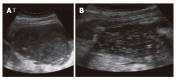
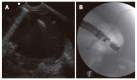
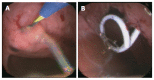
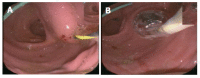
Methods: From 02/01/2002 to 05/31/2004, all consecutive patients with symptomatic PPC who underwent an interventional endoscopic approach were evaluated in this pilot case-series study: Group (Gr.) I-Primary percutaneous (external), ultrasound-guided drainage. Gr. II-Primary EUS-guided cystogastrostomy. Gr. III-EUS-guided cystogastrostomy including intracystic necrosectomy.
Results: (="follow up": n = 27): Gr. I (n = 9; 33.3%): No complaints (n = 3); change of an external into an internal drainage (n = 4); complications: (a) bleeding (n = 1) followed by 3 d at ICU, discharge after 40 d; (b) septic shock (n = 1) followed by ICU and several laparotomies for programmed lavage and necrosectomy, death after 74 d. Gr. II (n = 13; 48.1%): No complaints (n = 11); external drainage (n = 2); complications/problems out of the 13 cases: 2nd separate pseudocyst (n = 1) with external drainage (since no communication with primary internal drainage); infection of the residual cyst (n = 1) + following external drainage; spontaneous PPC perforation (n = 1) + following closure of the opening of the cystogastrostomy using clips and subsequently ICU for 2 d. Gr. III (n = 5; 18.5%): No complaints in all patients, in average two endoscopic procedures required (range, 2-6).
Conclusion: Interventional endoscopic management of pancreatic pseudocysts is a reasonable alternative treatment option with low invasiveness compared to surgery and an acceptable outcome with regard to the complication rate (11.1%) and mortality (3.7%), as shown by these initial study results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pancreatic pseudocyst drainage in children by image-guided cystogastrostomy and stent insertion.Pediatr Radiol. 2019 Dec;49(13):1816-1822. doi: 10.1007/s00247-019-04471-9. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Pediatr Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31342130 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome and complications of endoscopic ultrasound guided pancreatic pseudocyst drainage using combined endoprosthesis and naso-cystic drain.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Apr;27(4):722-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2012.07089.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22313377
-
A case report of giant pancreatic pseudocyst following acute pancreatitis: experience with endoscopic internal drainage.BMC Res Notes. 2018 Apr 27;11(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s13104-018-3375-9. BMC Res Notes. 2018. PMID: 29703250 Free PMC article.
-
EUS-guided drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts, abscesses and infected necrosis.Dig Endosc. 2009 Jul;21 Suppl 1:S61-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2009.00860.x. Dig Endosc. 2009. PMID: 19691738 Review.
-
Endoscopic Management of Peri-Pancreatic Fluid Collections.Gut Liver. 2017 Sep 15;11(5):604-611. doi: 10.5009/gnl16178. Gut Liver. 2017. PMID: 28494574 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current status of minimally invasive necrosectomy for post-inflammatory pancreatic necrosis.HPB (Oxford). 2009 Mar;11(2):96-102. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2009.00041.x. HPB (Oxford). 2009. PMID: 19590631 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Drainage without Fluoroscopic Guidance for Extraluminal Complicated Cysts.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016;2016:1249064. doi: 10.1155/2016/1249064. Epub 2016 May 30. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016. PMID: 27313606 Free PMC article.
-
EUS-Guided Multitransgastric Endoscopic Necrosectomy for Infected Pancreatic Necrosis with Noncontagious Retroperitoneal and Peritoneal Extension.Gut Liver. 2010 Mar;4(1):140-5. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2010.4.1.140. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Gut Liver. 2010. PMID: 20479929 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the endoscopic management of pancreatic collections.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Apr 16;7(4):381-8. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i4.381. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015. PMID: 25901217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of severe acute pancreatitis and its complications.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 14;20(38):13879-92. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13879. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25320523 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ammori BJ, Bhattacharya D, Senapati PS. Laparoscopic endogastric pseudocyst gastrostomy: a report of three cases. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2002;12:437–440. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya D, Ammori BJ. Minimally invasive approaches to the management of pancreatic pseudocysts: review of the literature. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2003;13:141–148. - PubMed
-
- Giovannini M, Binmoeller K, Seifert H. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided cystogastrostomy. Endoscopy. 2003;35:239–245. - PubMed
-
- Vosoghi M, Sial S, Garrett B, Feng J, Lee T, Stabile BE, Eysselein VE. EUS-guided pancreatic pseudocyst drainage: review and experience at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center. MedGenMed. 2002;4:2. - PubMed
-
- Baillie J. Pancreatic pseudocysts (Part I) Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;59:873–879. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

