Expression of angiopoietins, Tie2 and vascular endothelial growth factor in angiogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 16830384
- PMCID: PMC4087383
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i26.4241
Expression of angiopoietins, Tie2 and vascular endothelial growth factor in angiogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the significance of angiopoietins, Tie2 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in the angiogenesis and progress of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: Fresh surgically resected specimens of HCC and noncancerous liver (NCL) tissue from 38 patients with HCC were obtained, and expression of angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1), angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2), Tie2, and VEGF messenger RNA (mRNA) was examined by real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Expression pattern of each gene in HCC and NCL tissue specimens was compared and the potential role and interaction in angiogenesis of HCC were analyzed. Genes' expression level and its relationship with tumor's clinicopathological parameters were also investigated. Immunohistochemical staining of CD34 was performed to determine the microvessel density (MVD) and Ang-2/Ang-1 ratio was calculated. Relationships between Ang-2/Ang-1 ratio, VEGF and MVD and clinicopathological features were also tested so as to evaluate their significance in the progression of HCC.
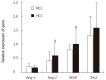
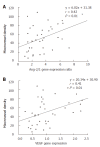
Results: Ang-2 and VEGF mRNAs in HCC were significantly higher than those in NCL tissue (P < 0.05), whereas the Ang-1 and Tie2 mRNAs showed no statistical significance (P > 0.05), though slightly lower level of Ang-1 mRNA in HCC was observed. Ang-2/Ang-1 ratio and VEGF were both positively correlated to MVD. The Ang-2/ Ang-1 ratio, Ang-2 and VEGF were all associated with tumor's clinicopathological parameters (P < 0.05) except for histological grades (P > 0.05). Ang-1 and Tie2 levels in different clinicopathological groups were not significantly different (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Dominant Ang-2 expression against Ang-1 through Tie2 receptor in the presence of VEGF plays a critical role in initiating early neovascularization and transformation of noncancerous liver to hepatocellular carcinoma. Its consequently constant operation in formed HCC induces further angiogenesis and progression of HCC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Angiopoietin/Tie2 Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cells. 2020 Oct 30;9(11):2382. doi: 10.3390/cells9112382. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33143149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression pattern of angiogenic factors and prognosis after hepatic resection in hepatocellular carcinoma: importance of angiopoietin-2 and hypoxia-induced factor-1 alpha.Liver Int. 2006 May;26(4):414-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2006.01243.x. Liver Int. 2006. PMID: 16629644
-
Angiopoietin switching regulates angiogenesis and progression of human hepatocellular carcinoma.J Clin Pathol. 2003 Nov;56(11):854-60. doi: 10.1136/jcp.56.11.854. J Clin Pathol. 2003. PMID: 14600132 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the angopoietin-1, angopoietin-2, Tie2, and vascular endothelial growth factor gene in epithelial ovarian cancer.Gynecol Oncol. 2004 Apr;93(1):215-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2003.12.031. Gynecol Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15047239
-
Angiopoietins/Tie2 signaling axis and its role in angiogenesis of psoriasis.Acta Histochem. 2025 Mar;127(1):152228. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2024.152228. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Acta Histochem. 2025. PMID: 39752990 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism-related circulating proteins as biomarkers for clinical outcome in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma receiving sunitinib.J Transl Med. 2011 Jul 25;9:120. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-120. J Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21787417 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth in vitro and in vivo using an anti-angiopoietin-2 single-chain antibody.Exp Ther Med. 2014 Mar;7(3):543-552. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.1476. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Exp Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 24520243 Free PMC article.
-
The Angiopoietin/Tie2 Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cells. 2020 Oct 30;9(11):2382. doi: 10.3390/cells9112382. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33143149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vasomics of the liver.Gut. 2025 May 7;74(6):1008-1020. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2024-334133. Gut. 2025. PMID: 40044498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: hurdles, advances and prospects.Hepat Oncol. 2018 Sep 28;5(2):HEP08. doi: 10.2217/hep-2018-0002. eCollection 2018 Apr. Hepat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 31293776 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pisani P, Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J. Erratum: Estimates of the worldwide mortality from 25 cancers in 1990. Int. J. Cancer, 83, 18-29 (1999) Int J Cancer. 1999;83:870–873. - PubMed
-
- Poon RT, Ng IO, Lau C, Yu WC, Fan ST, Wong J. Correlation of serum basic fibroblast growth factor levels with clinicopathologic features and postoperative recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Surg. 2001;182:298–304. - PubMed
-
- Poon RT, Lau CP, Ho JW, Yu WC, Fan ST, Wong J. Tissue factor expression correlates with tumor angiogenesis and invasiveness in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:5339–5345. - PubMed
-
- Carr BI. Hepatocellular carcinoma: current management and future trends. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S218–S224. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

