Delayed hemorrhage from hepatic artery after ultrasound-guided percutaneous liver biopsy: a case report
- PMID: 16830394
- PMCID: PMC4087393
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i26.4273
Delayed hemorrhage from hepatic artery after ultrasound-guided percutaneous liver biopsy: a case report
Abstract
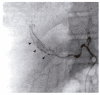
Percutaneous liver biopsy is considered one of the most important diagnostic tools to evaluate diffuse liver diseases. Pseudoaneurysm of hepatic artery is an unusual complication after ultrasound-guided percutaneous liver biopsy. Delayed hemorrhage occurs much less frequently. We report a case of pseudoaneurysm of the hepatic artery of a 46-year-old man who was admitted for abdominal pain after 4 d of liver biopsy. The bleeding was controlled initially by angiographic embolization. However, recurrent bleeding could not be controlled by repeat angiography, and the patient died 4 d after admission from multiorgan failure. The admittedly rare possibility of delayed hemorrhage should be considered whenever a liver biopsy is performed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Delayed fatal hemorrhage from pseudoaneurysm of the hepatic artery after percutaneous liver biopsy.Am J Gastroenterol. 2001 Jan;96(1):233-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.03482.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11197259
-
Delayed hemorrhage after percutaneous liver biopsy. Role of therapeutic angiography.J Clin Gastroenterol. 1994 Jul;19(1):50-3. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199407000-00013. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1994. PMID: 7930434
-
Gastrointestinal hemorrhage caused by rupture of a pseudoaneurysm of the hepatic artery.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2012 Apr;23(2):160-4. doi: 10.4318/tjg.2012.0460. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22706745
-
Traumatic pseudoaneurysms of the liver and spleen in children: is routine screening warranted?J Pediatr Surg. 2011 May;46(5):938-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2011.02.035. J Pediatr Surg. 2011. PMID: 21616256 Review.
-
Intercostal artery pseudoaneurysm after ultrasound-guided liver biopsy: a case report and review of the literature.Ultrasound Q. 2015 Mar;31(1):63-5. doi: 10.1097/RUQ.0000000000000074. Ultrasound Q. 2015. PMID: 25706367 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy With Needle Track Plugging in Patients With Focal Liver Lesions on an Outpatient Basis: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Korean J Radiol. 2024 Oct;25(10):902-912. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2024.0536. Korean J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 39344547 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hemothorax caused by injury of musculophrenic artery after ultrasound-guided percutaneous liver biopsy: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2024 Jun 26;18(1):303. doi: 10.1186/s13256-024-04619-8. J Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38918846 Free PMC article.
-
Post biopsy delayed liver hemorrhage successfully controlled by bedside CEUS-guided microwave ablation: A case report.Clin Case Rep. 2023 Feb 8;11(2):e6916. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.6916. eCollection 2023 Feb. Clin Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36789325 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding and hepatic infarction after liver biopsy.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Feb 21;20(7):1878-81. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1878. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24587666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McGill DB, Rakela J, Zinsmeister AR, Ott BJ. A 21-year experience with major hemorrhage after percutaneous liver biopsy. Gastroenterology. 1990;99:1396–1400. - PubMed
-
- Younossi ZM, Teran JC, Ganiats TG, Carey WD. Ultrasound-guided liver biopsy for parenchymal liver disease: an economic analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 1998;43:46–50. - PubMed
-
- Farrell RJ, Smiddy PF, Pilkington RM, Tobin AA, Mooney EE, Temperley IJ, McDonald GS, Bowmer HA, Wilson GF, Kelleher D. Guided versus blind liver biopsy for chronic hepatitis C: clinical benefits and costs. J Hepatol. 1999;30:580–587. - PubMed
-
- Rossi P, Sileri P, Gentileschi P, Sica GS, Forlini A, Stolfi VM, De Majo A, Coscarella G, Canale S, Gaspari AL. Percutaneous liver biopsy using an ultrasound-guided subcostal route. Dig Dis Sci. 2001;46:128–132. - PubMed
-
- Reichert CM, Weisenthal LM, Klein HG. Delayed hemorrhage after percutaneous liver biopsy. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1983;5:263–266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical