Insulin activates human sterol-regulatory-element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) promoter through SRE motifs
- PMID: 16831124
- PMCID: PMC1635455
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20060499
Insulin activates human sterol-regulatory-element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) promoter through SRE motifs
Abstract
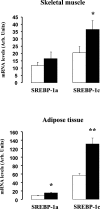
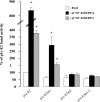
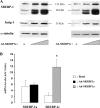
In the present study, we aimed to decipher the mechanisms involved in the transcriptional effect of insulin on the SREBP-1c specific promoter of the human srebf-1 gene. Using luciferase reporter gene constructs in HEK-293 cells (human embryonic kidney cells), we demonstrated that the full effect of insulin requires the presence of SREs (sterol response elements) in the proximal region of the promoter. Furthermore, insulin increases the binding of SREBP-1 (sterol-regulatory-element-binding protein-1) to this promoter region in chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. We also found that the nuclear receptors LXRs (liver X receptors) strongly activate SREBP-1c gene expression and identified the LXRE (LXR-response element) involved in this effect. However, our results suggested that these LXREs do not play a major role in the response to insulin. Finally, using expression vectors and adenoviruses allowing ectopic overexpressions of the human mature forms of SREBP-1a or SREBP-1c, we demonstrated the direct role of SREBP-1 in the control of SREBP-1c gene expression in human skeletal-muscle cells. Altogether, these results strongly suggest that the SREBP-1 transcription factors are the main mediators of insulin action on SREBP-1c expression in human tissues.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Microarray analyses of SREBP-1a and SREBP-1c target genes identify new regulatory pathways in muscle.Physiol Genomics. 2008 Aug 15;34(3):327-37. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.90211.2008. Epub 2008 Jun 17. Physiol Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18559965
-
Regulation of GLUT4 gene expression by SREBP-1c in adipocytes.Biochem J. 2006 Oct 1;399(1):131-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20060696. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16787385 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of LPL gene expression by sterols is mediated by a sterol regulatory element and is independent of the presence of multiple E boxes.J Mol Biol. 2000 Dec 1;304(3):323-34. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4218. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 11090277
-
[Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism by insulin: role of transcription factor SREBP-1c in the hepatic transcriptional effects of the hormone].J Soc Biol. 2001;195(3):243-8. J Soc Biol. 2001. PMID: 11833461 Review. French.
-
Retinoic acid-mediated transcription and maturation of SREBP-1c regulates fatty acid synthase via cis-elements responsible for nutritional regulation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Nov;35(Pt 5):1211-4. doi: 10.1042/BST0351211. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 17956315 Review.
Cited by
-
Orphan nuclear receptor DAX-1 acts as a novel corepressor of liver X receptor alpha and inhibits hepatic lipogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 19;285(12):9221-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.073650. Epub 2010 Jan 15. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20080977 Free PMC article.
-
Bone muscle crosstalk targets muscle regeneration pathway regulated by core circadian transcriptional repressors DEC1 and DEC2.Bonekey Rep. 2016 Nov 16;5:850. doi: 10.1038/bonekey.2016.80. eCollection 2016. Bonekey Rep. 2016. PMID: 27867498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DHT causes liver steatosis via transcriptional regulation of SCAP in normal weight female mice.J Endocrinol. 2021 Jun 28;250(2):49-65. doi: 10.1530/JOE-21-0040. J Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34060475 Free PMC article.
-
Diverging metabolic effects of 2 energy-restricted diets differing in nutrient quality: a 12-week randomized controlled trial in subjects with abdominal obesity.Am J Clin Nutr. 2022 Jul 6;116(1):132-150. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqac025. Am J Clin Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35102369 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term statins administration exacerbates diabetic nephropathy via ectopic fat deposition in diabetic mice.Nat Commun. 2023 Jan 24;14(1):390. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-35944-z. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36693830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Brien R. M., Granner D. K. Regulation of gene expression by insulin. Physiol. Rev. 1996;76:1109–1161. - PubMed
-
- Rome S., Clement K., Rabasa-Lhoret R., Loizon E., Poitou C., Barsh G. S., Riou J. P., Laville M., Vidal H. Microarray profiling of human skeletal muscle reveals that insulin regulates approximately 800 genes during a hyperinsulinemic clamp. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:18063–18068. - PubMed
-
- Ducluzeau P. H., Perretti N., Laville M., Andreelli F., Vega N., Riou J. P., Vidal H. Regulation by insulin of gene expression in human skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Evidence for specific defects in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2001;50:1134–1142. - PubMed
-
- Patti M. E. Gene expression in humans with diabetes and prediabetes: what have we learned about diabetes pathophysiology? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 2004;7:383–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

