Low testosterone levels and the risk of anemia in older men and women
- PMID: 16832003
- PMCID: PMC2645631
- DOI: 10.1001/archinte.166.13.1380
Low testosterone levels and the risk of anemia in older men and women
Abstract
Background: Anemia is a frequent feature of male hypogonadism and anti-androgenic treatment. We hypothesized that the presence of low testosterone levels in older persons is a risk factor for anemia.
Methods: Testosterone and hemoglobin levels were measured in a representative sample of 905 persons 65 years or older without cancer, renal insufficiency, or anti-androgenic treatments. Hemoglobin levels were reassessed after 3 years.
Results: At baseline, 31 men and 57 women had anemia. Adjusting for confounders, we found that total and bioavailable testosterone levels were associated with hemoglobin levels in women (P = .001 and P = .02, respectively) and in men (P<.001 and P = .03, respectively). Men and women in the lowest quartile of total and bioavailable testosterone were more likely than those in the highest to have anemia (men, 14/99 vs 3/100; odds ratio [OR], 5.4; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.4-21.8 for total and 16/99 vs 1/99; OR, 13.1; 95% CI, 1.5-116.9 for bioavailable testosterone; women, 21/129 vs 12/127; OR, 2.1; 95% CI, 0.9-5.0 for total and 24/127 vs 6/127; OR, 3.4; 95% CI, 1.2-9.4 for bioavailable testosterone). Among nonanemic participants and independent of confounders, men and women with low vs normal total and bioavailable testosterone levels had a significantly higher risk of developing anemia at 3-year follow-up (21/167 vs 28/444; relative risk, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.1-4.1 for total and 26/143 vs 23/468; relative risk, 3.9; 95% CI, 1.9-7.8 for bioavailable testosterone).
Conclusion: Older men and women with low testosterone levels have a higher risk of anemia.
Figures
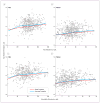
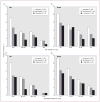
Similar articles
-
Relationship between low levels of anabolic hormones and 6-year mortality in older men: the aging in the Chianti Area (InCHIANTI) study.Arch Intern Med. 2007 Nov 12;167(20):2249-54. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.20.2249. Arch Intern Med. 2007. PMID: 17998499 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Testosterone Levels With Anemia in Older Men: A Controlled Clinical Trial.JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Apr 1;177(4):480-490. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.9540. JAMA Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28241237 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Association of Low Hemoglobin Levels with IgA Nephropathy Progression: A Two-Center Cohort Study of 1,828 Cases.Am J Nephrol. 2020;51(8):624-634. doi: 10.1159/000508770. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Am J Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32694247
-
Low Hemoglobin Levels and Risk of Developing Depression in the Elderly: Results From the Prospective PRO.V.A. Study.J Clin Psychiatry. 2016 Dec;77(12):e1549-e1556. doi: 10.4088/JCP.15m10270. J Clin Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27835718
-
Anemia and hemoglobin levels in older persons: relationship with age, gender, and health status.J Am Geriatr Soc. 1992 May;40(5):489-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1992.tb02017.x. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1992. PMID: 1634703
Cited by
-
Risks and benefits of testosterone therapy in older men.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013 Jul;9(7):414-24. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2013.73. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23591366 Review.
-
Anemia in Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Prevalence, pathogenesis, and potential impact.Lung India. 2015 Mar-Apr;32(2):142-51. doi: 10.4103/0970-2113.152626. Lung India. 2015. PMID: 25814799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hematopoiesis, Inflammation and Aging-The Biological Background and Clinical Impact of Anemia and Increased C-Reactive Protein Levels on Elderly Individuals.J Clin Med. 2022 Jan 28;11(3):706. doi: 10.3390/jcm11030706. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35160156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A randomized trial of adjunct testosterone for cancer-related muscle loss in men and women.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018 Jun;9(3):482-496. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12295. Epub 2018 Apr 14. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018. PMID: 29654645 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Serum Ferritin Is Inversely Correlated with Testosterone in Boys and Young Male Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study in Taiwan.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 8;10(12):e0144238. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144238. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26646112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shahidi NT. Androgens and erythropoiesis. N Engl J Med. 1973;289:72–80. - PubMed
-
- Krabbe S, Christensen T, Worm J, Christiansen C, Transbol I. Relationship between haemoglobin and serum testosterone in normal children and adolescents and in boys with delayed puberty. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1978;67:655–658. - PubMed
-
- Hero M, Wickman S, Hanhijarvi R, Siimes MA, Dunkel L. Pubertal upregulation of erythropoiesis in boys is determined primarily by androgen. J Pediatr. 2005;146:245–252. - PubMed
-
- Fonseca R, Rajkumar SV, White WL, Tefferi A, Hoagland HC. Anemia after orchiectomy. Am J Hematol. 1998;59:230–233. - PubMed
-
- Ornstein DK, Beiser JA, Andriole GL. Anaemia in men receiving combined finasteride and flutamide therapy for advanced prostate cancer. BJU Int. 1999;83:43–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

