WNK1 and OSR1 regulate the Na+, K+, 2Cl- cotransporter in HeLa cells
- PMID: 16832045
- PMCID: PMC1544143
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0604607103
WNK1 and OSR1 regulate the Na+, K+, 2Cl- cotransporter in HeLa cells
Abstract
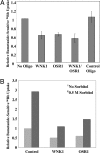
Oxidative stress-responsive kinase (OSR) 1 and sterile20-related, proline-, alanine-rich kinase (SPAK) are Ste20p-related protein kinases that bind to the sodium, potassium, two chloride cotransporter, NKCC. Here we present evidence that the protein kinase with no lysine [K] (WNK) 1 regulates OSR1, SPAK, and NKCC activities. OSR1 exists in a complex with WNK1 in cells, is activated by recombinant WNK1 in vitro, and is phosphorylated in a WNK1-dependent manner in cells. Depletion of WNK1 from HeLa cells by using small interfering RNA reduces OSR1 kinase activity. In addition, depletion of either WNK1 or OSR1 reduces NKCC activity, indicating that WNK1 and OSR1 are both required for NKCC function. OSR1 and SPAK are likely links between WNK1 and NKCC in a pathway that contributes to volume regulation and blood pressure homeostasis in mammals.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

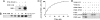
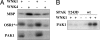
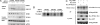
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

