Two-dimensional nanoparticle arrays show the organizational power of robust DNA motifs
- PMID: 16834438
- PMCID: PMC3465979
- DOI: 10.1021/nl060994c
Two-dimensional nanoparticle arrays show the organizational power of robust DNA motifs
Abstract
The bottom-up spatial organization of potential nanoelectronic components is a key intermediate step in the development of molecular electronics. We describe robust three-space-spanning DNA motifs that are used to organize nanoparticles in two dimensions. One strand of the motif ends in a gold nanoparticle; only one DNA strand is attached to the particle. By using two of the directions of the motif to produce a two-dimensional crystalline array, one direction is free to bind gold nanoparticles. Identical motifs, tailed in different sticky ends, enable the two-dimensional periodic ordering of 5 and 10 nm diameter gold nanoparticles.
Figures
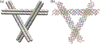
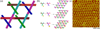

Similar articles
-
Periodic square-like gold nanoparticle arrays templated by self-assembled 2D DNA Nanogrids on a surface.Nano Lett. 2006 Feb;6(2):248-51. doi: 10.1021/nl052210l. Nano Lett. 2006. PMID: 16464044
-
Switching binary states of nanoparticle superlattices and dimer clusters by DNA strands.Nat Nanotechnol. 2010 Feb;5(2):116-20. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2009.378. Epub 2009 Dec 20. Nat Nanotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20023646
-
Covalent Linkage of One-Dimensional DNA Arrays Bonded by Paranemic Cohesion.ACS Nano. 2015 Oct 27;9(10):10304-12. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b04335. Epub 2015 Sep 11. ACS Nano. 2015. PMID: 26343906
-
At the crossroads of chemistry, biology, and materials: structural DNA nanotechnology.Chem Biol. 2003 Dec;10(12):1151-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2003.12.002. Chem Biol. 2003. PMID: 14700623 Review.
-
Patterning metallic nanoparticles by DNA scaffolds.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;620:107-16. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-76713-0_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 18217338 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA-linked superlattices get into shape.Nat Mater. 2015 Aug;14(8):746-9. doi: 10.1038/nmat4376. Nat Mater. 2015. PMID: 26201879 No abstract available.
-
Combing and self-assembly phenomena in dry films of Taxol-stabilized microtubules.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2007 Mar 13;2(3):135-43. doi: 10.1007/s11671-007-9044-x. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2007. PMID: 21806849 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembly of biomolecular soft matter.Faraday Discuss. 2013;166:9-30. doi: 10.1039/c3fd00120b. Faraday Discuss. 2013. PMID: 24611266 Free PMC article.
-
Designer DNA nanoarchitectures.Biochemistry. 2009 Mar 3;48(8):1663-74. doi: 10.1021/bi802324w. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19199428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Position Accuracy of Gold Nanoparticles on DNA Origami Structures Studied with Small-Angle X-ray Scattering.Nano Lett. 2018 Apr 11;18(4):2609-2615. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b00412. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Nano Lett. 2018. PMID: 29498287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alivisatos AP. J. Phys. Chem. 1996;100:13226–13239.
- Redl FX, Cho KS, Murray CB, O'Brien S. Nature. 2003;423:978–971. - PubMed
-
- Kiehl RA. J. Nanopart. Res. 2000;2:331–332.
-
- Likharev KK. Electronics Below 10 nm. In: Greer J, Korkin A, Labanowski J, editors. Nano and Giga Challenges in Microelectronics. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2003. pp. 27–68.
- Maier SA, Brongersma ML, Kik PG, Meltzer S, Requicha AAG, Atwater HA. Adv. Mater. 2001;13:1501–1505.
- Shipway AN, Katz E, Willner I. ChemPhysChem. 2000;1:18–52. - PubMed
-
- Alivisatos A, Johnsson K, Peng X, Wilson T, Lowth C, Bruchez M, Schultz P. Nature. 1996;382:609–611. - PubMed
- Loweth C, Caldwell W, Peng X, Alivisatos P, Schultz P. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999;38:1808–1812. - PubMed
- Zanchet D, Micheel C, Parak W, Alivisatos P. Nano Lett. 2001;1:32–35.
- Zanchet D, Micheel C, Parak W, Alivisatos P. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2002;106:11758–11763.
-
- Mucic R, Storhoff J, Letsinger R, Mirkin C. Nature. 1996;382:607–609. - PubMed
- Storhoff J, Elghenian R, Mucic R, Mirkin C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998;120:1959–1964.
- Jin R, Wu G, Li Z, Mirkin C, Schatz G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:1643–1654. - PubMed
- Anderson CJ, Sykes TJ, Kornberg RD. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA) 2005;102:13383–13385. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

