Streptococcus pneumoniae induced c-Jun-N-terminal kinase- and AP-1 -dependent IL-8 release by lung epithelial BEAS-2B cells
- PMID: 16834785
- PMCID: PMC1533820
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-98
Streptococcus pneumoniae induced c-Jun-N-terminal kinase- and AP-1 -dependent IL-8 release by lung epithelial BEAS-2B cells
Abstract
Background: Although pneumococcal pneumonia is one of the most common causes of death due to infectious diseases, little is known about pneumococci-lung cell interaction. Herein we tested the hypothesis that pneumococci activated pulmonary epithelial cell cytokine release by c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) METHODS: Human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) or epithelial HEK293 cells were infected with S. pneumoniae R6x and cytokine induction was measured by RT-PCR, ELISA and Bioplex assay. JNK-phosphorylation was detected by Western blot and nuclear signaling was assessed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). JNK was modulated by the small molecule inhibitor SP600125 and AP1 by transfection of a dominant negative mutant.
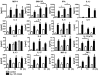
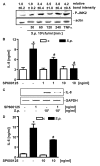
Results: S. pneumoniae induced the release of distinct CC and CXC, as well as Th1 and Th2 cytokines and growth factors by human lung epithelial cell line BEAS-2B. Furthermore, pneumococci infection resulted in JNK phosphorylation in BEAS-2B cells. Inhibition of JNK by small molecule inhibitor SP600125 reduced pneumococci-induced IL-8 mRNA expression and release of IL-8 and IL-6. One regulator of the il8 promoter is JNK-phosphorylated activator protein 1 (AP-1). We showed that S. pneumoniae time-dependently induced DNA binding of AP-1 and its phosphorylated subunit c-Jun with a maximum at 3 to 5 h after infection. Recruitment of Ser63/73-phosphorylated c-Jun and RNA polymerase II to the endogenous il8 promoter was found 2 h after S. pneumoniae infection by chromatin immunoprecipitation. AP-1 repressor A-Fos reduced IL-8 release by TLR2-overexpressing HEK293 cells induced by pneumococci but not by TNFalpha. Antisense-constructs targeting the AP-1 subunits Fra1 and Fra2 had no inhibitory effect on pneumococci-induced IL-8 release.
Conclusion: S. pneumoniae-induced IL-8 expression by human epithelial BEAS-2B cells depended on activation of JNK and recruitment of phosphorylated c-Jun to the il8 promoter.
Figures

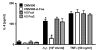
Similar articles
-
IL-1beta induces MMP-9 expression via a Ca2+-dependent CaMKII/JNK/c-JUN cascade in rat brain astrocytes.Glia. 2009 Dec;57(16):1775-89. doi: 10.1002/glia.20890. Glia. 2009. PMID: 19455716
-
Peptidoglycan induces interleukin-6 expression through the TLR2 receptor, JNK, c-Jun, and AP-1 pathways in microglia.J Cell Physiol. 2011 Jun;226(6):1573-82. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22489. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 20945380
-
Pneumococci induced TLR- and Rac1-dependent NF-kappaB-recruitment to the IL-8 promoter in lung epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006 Apr;290(4):L730-L737. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00271.2005. Epub 2005 Nov 18. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16299055
-
TNF-alpha production in the skin.Arch Dermatol Res. 2009 Jan;301(1):87-91. doi: 10.1007/s00403-008-0893-7. Epub 2008 Sep 30. Arch Dermatol Res. 2009. PMID: 18825399 Review.
-
Inhibitors of c-Jun N-terminal kinases: JuNK no more?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jan;1784(1):76-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.09.013. Epub 2007 Oct 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 17964301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Streptococcus pneumoniae adherence to human epithelial cells in vitro by the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG.BMC Res Notes. 2013 Apr 5;6:135. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-135. BMC Res Notes. 2013. PMID: 23561014 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology to dissect the mechanisms of Yinlai Decoction for pneumonia.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Jun 3;20(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02954-z. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32493296 Free PMC article.
-
NEDD4 Regulated Pyroptosis Occurred from Co-infection between Influenza A Virus and Streptococcus pneumoniae.J Microbiol. 2023 Aug;61(8):777-789. doi: 10.1007/s12275-023-00076-y. Epub 2023 Oct 4. J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37792248
-
Antibacterial Effects of Phage Lysin LysGH15 on Planktonic Cells and Biofilms of Diverse Staphylococci.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Jul 17;84(15):e00886-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00886-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29776929 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting cellular senescence and SASP in Drosophila.Inflamm Regen. 2016 Dec 5;36:25. doi: 10.1186/s41232-016-0031-4. eCollection 2016. Inflamm Regen. 2016. PMID: 29259698 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Obaro S, Adegbola R. The pneumococcus: carriage, disease and conjugate vaccines. J Med Microbiol. 2002;51:98–104. - PubMed
-
- The world health report 1996 http://www.who.int/whr/1996/en/index.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

