Contacts and cooperation between cells depend on the hormone ouabain
- PMID: 16835298
- PMCID: PMC1544148
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0604496103
Contacts and cooperation between cells depend on the hormone ouabain
Abstract
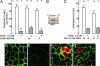
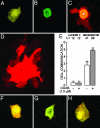
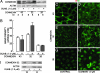
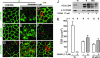
Cell adhesion is a crucial step in proliferation, differentiation, migration, apoptosis, and metastasis. In previous works we have shown that cell adhesion is modulated by ouabain, a highly specific inhibitor of Na+,K+-ATPase, recently found to be a hormone. In the present work we pursue the investigation of the effect of ouabain on a special type of cell-cell interaction: the rescue of ouabain-sensitive MDCK cells (W) by ouabain-resistant cells (R). In cultured monolayers of pure W cells, ouabain triggers the "P-->A mechanism" (from pump/adhesion) consisting of a cascade of phosphorylations that retrieves adhesion-associated molecules occludin and beta-catenin and results in detachment of the cell. When W cells are instead cocultured with R cells, the P-->A reaction is blocked, and W cells are rescued. Furthermore, in these R/W cocultures ouabain promotes cell-cell communication by means of gap junctions by specifically enhancing the expression of connexin 32 and addressing this molecule to the plasma membrane. Ouabain also promotes the internalization of the beta-subunit of the Na+,K+-ATPase. These observations open the possibility that the crucial processes mentioned at the beginning would be under the control of the hormone ouabain.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ouabain modulates cell contacts as well as functions that depend on cell adhesion.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;763:155-68. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-191-8_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21874450
-
Rescue of a wild-type MDCK cell by a ouabain-resistant mutant.Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 1):C151-61. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.1.C151. Am J Physiol. 1987. PMID: 3300360
-
Ouabain Modulates the Distribution of Connexin 43 in Epithelial Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(4):1329-38. doi: 10.1159/000447837. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27606882
-
Ouabain increases gap junctional communication in epithelial cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34(6):2081-90. doi: 10.1159/000366403. Epub 2014 Nov 28. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 25562156
-
Na+,K+-ATPase and hormone ouabain:new roles for an old enzyme and an old inhibitor.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2006 Dec 30;52(8):31-40. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2006. PMID: 17535734 Review.
Cited by
-
The cardiotonic steroid hormone marinobufagenin induces renal fibrosis: implication of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009 Apr;296(4):F922-34. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.90605.2008. Epub 2009 Jan 28. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19176701 Free PMC article.
-
Gap junctional signaling in pattern regulation: Physiological network connectivity instructs growth and form.Dev Neurobiol. 2017 May;77(5):643-673. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22405. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Dev Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27265625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ouabain Induces Transcript Changes and Activation of RhoA/ROCK Signaling in Cultured Epithelial Cells (MDCK).Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Sep 14;45(9):7538-7556. doi: 10.3390/cimb45090475. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37754259 Free PMC article.
-
Ouabain Accelerates Collective Cell Migration Through a cSrc and ERK1/2 Sensitive Metalloproteinase Activity.J Membr Biol. 2019 Dec;252(6):549-559. doi: 10.1007/s00232-019-00066-5. Epub 2019 Apr 30. J Membr Biol. 2019. PMID: 31041466
-
Glutamate transporter coupling to Na,K-ATPase.J Neurosci. 2009 Jun 24;29(25):8143-55. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1081-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19553454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schatzmann H. J. Helv. Physiol. Pharmacol. Acta. 1953;11:346–354. - PubMed
-
- Skou J. C. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1957;23:394–401. - PubMed
-
- Schoner W., Bauer N., Muller-Ehmsen J., Kramer U., Hambarchian N., Schwinger R., Moeller H., Kost H., Weitkamp C., Schweitzer T., et al. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2003;986:678–684. - PubMed
-
- Bauer N., Muller-Ehmsen J., Kramer U., Hambarchian N., Zobel C., Schwinger R. H., Neu H., Kirch U., Grunbaum E. G., Schoner W. Hypertension. 2005;45:1024–1028. - PubMed
-
- Hamlyn J. M., Manunta P. J. Hypertens. Suppl. 1992;10:S99–S111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

