Cell cycle regulator E2F1 modulates angiogenesis via p53-dependent transcriptional control of VEGF
- PMID: 16835303
- PMCID: PMC1544166
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0509533103
Cell cycle regulator E2F1 modulates angiogenesis via p53-dependent transcriptional control of VEGF
Abstract
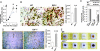
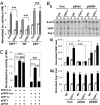
The transcription factor E2F1 is known to regulate cell proliferation and has been thought to modulate tumorigenesis via this mechanism alone. Here we show that mice deficient in E2F1 exhibit enhanced angiogenesis. The proangiogenic phenotype in E2F1 deficiency is the result of overproduction of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and is prevented by VEGF blockade. Under hypoxic conditions, E2F1 down-regulates the expression of VEGF promoter activity by associating with p53 and specifically down-regulating expression of VEGF but not other hypoxia-inducible genes, suggesting a promoter structure context-dependent regulation mechanism. We found that the minimum VEGF promoter mediating transcriptional repression by E2F1 features an E2F1- binding site with four Sp-1 sites in close proximity. These data disclose an unexpected function of endogenous E2F1: regulation of angiogenic activity via p53-dependent transcriptional control of VEGF expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
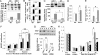

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL077428/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080137/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL057516/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-57516/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-53354/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL066957/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL063414/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-80137/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-77428/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-66957/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL053354/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-63414/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL053354/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

