FsFKS1, the 1,3-beta-glucan synthase from the caspofungin-resistant fungus Fusarium solani
- PMID: 16835448
- PMCID: PMC1489279
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00030-06
FsFKS1, the 1,3-beta-glucan synthase from the caspofungin-resistant fungus Fusarium solani
Abstract
The cell wall, a mesh of carbohydrates and proteins, shapes and protects the fungal cell. The enzyme responsible for the synthesis of one of the main components of the fungal wall, 1,3-beta-glucan synthase, is targeted by the antifungal caspofungin acetate (CFA). Clinical isolates of Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus are much more sensitive to CFA than clinical isolates of Fusarium species. To better understand CFA resistance in Fusarium species, we cloned and sequenced FsFKS1, which encodes the Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi beta(1,3)-D-glucan synthase, used RNA interference to reduce its expression and complemented deletion of the essential fks gene of the CFA-sensitive fungus A. fumigatus with FsFKS1. Reduction of the FsFKS1 message in F. solani f. sp. pisi reduced spore viability and caused lysis of spores and hyphae, consistent with cell wall defects. Compensating for the loss of A. fumigatus fks1 with FsFKS1 caused only a modest increase in the tolerance of A. fumigatus for CFA. Our results suggest that FsFKS1 is required for the proper construction of F. solani cell walls and that the resistance of F. solani to CFA is at best only partially due to resistance of the FsFKS1 enzyme to this antifungal agent.
Figures
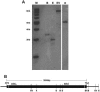

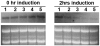
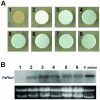
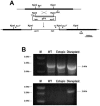
Similar articles
-
Role for Fks1 in the intrinsic echinocandin resistance of Fusarium solani as evidenced by hybrid expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 May;53(5):1772-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00020-09. Epub 2009 Mar 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19258277 Free PMC article.
-
The Paradoxical Effect of Echinocandins in Aspergillus fumigatus Relies on Recovery of the β-1,3-Glucan Synthase Fks1.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Jan 24;61(2):e01690-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01690-16. Print 2017 Feb. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 27872079 Free PMC article.
-
Specific substitutions in the echinocandin target Fks1p account for reduced susceptibility of rare laboratory and clinical Candida sp. isolates.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Aug;49(8):3264-73. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.8.3264-3273.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16048935 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Characterization of Aspergillus fumigatus mutants with reduced susceptibility to caspofungin.Med Mycol. 2005 May;43 Suppl 1:S299-305. doi: 10.1080/13693780400029023. Med Mycol. 2005. PMID: 16110824 Review.
-
Resistance in human pathogenic yeasts and filamentous fungi: prevalence, underlying molecular mechanisms and link to the use of antifungals in humans and the environment.Dan Med J. 2016 Oct;63(10):B5288. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27697142 Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing RNA interference for the control of Fusarium species: A critical review.Mol Plant Pathol. 2024 Oct;25(10):e70011. doi: 10.1111/mpp.70011. Mol Plant Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39363756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA microarray based on arrayed-primer extension technique for identification of pathogenic fungi responsible for invasive and superficial mycoses.J Clin Microbiol. 2008 Mar;46(3):909-15. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01406-07. Epub 2007 Dec 26. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18160452 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal echinocandin resistance.Fungal Genet Biol. 2010 Feb;47(2):117-26. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2009.09.003. Epub 2009 Sep 19. Fungal Genet Biol. 2010. PMID: 19770064 Free PMC article.
-
Host-induced gene silencing: a tool for understanding fungal host interaction and for developing novel disease control strategies.Mol Plant Pathol. 2012 Jun;13(5):519-29. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00766.x. Epub 2011 Nov 24. Mol Plant Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22111693 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo trans-specific gene silencing in fungal cells by in planta expression of a double-stranded RNA.BMC Biol. 2010 Mar 31;8:27. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-8-27. BMC Biol. 2010. PMID: 20356372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bozzola, J. J., R. J. Mehta, L. J. Nisbet, and J. R. Valenta. 1984. The effect of aculeacin A and papulacandin B on morphology and cell wall ultrastructure in Candida albicans. Can. J. Microbiol. 30:857-863. - PubMed
-
- Covert, S. F., J. Enkerli, V. P. Miao, and H. D. VanEtten. 1996. A gene for maackiain detoxification from a dispensable chromosome of Nectria haematococca. Mol. Gen. Genet. 251:397-406. - PubMed
-
- Douglas, C. M. 2001. Fungal beta(1,3)-d-glucan synthesis. Med. Mycol. 39(Suppl. 1):55-66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

