Farnesyl diphosphate synthase is a cytosolic enzyme in Leishmania major promastigotes and its overexpression confers resistance to risedronate
- PMID: 16835450
- PMCID: PMC1489282
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00034-06
Farnesyl diphosphate synthase is a cytosolic enzyme in Leishmania major promastigotes and its overexpression confers resistance to risedronate
Abstract
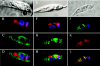
Farnesyl diphosphate synthase is the most likely molecular target of aminobisphosphonates (e.g., risedronate), a set of compounds that have been shown to have antiprotozoal activity both in vitro and in vivo. This protein, together with other enzymes involved in isoprenoid biosynthesis, is an attractive drug target, yet little is known about the compartmentalization of the biosynthetic pathway. Here we show the intracellular localization of the enzyme in wild-type Leishmania major promastigote cells and in transfectants overexpressing farnesyl diphosphate synthase by using purified antibodies generated towards a homogenous recombinant Leishmania major farnesyl diphosphate synthase protein. Indirect immunofluorescence, together with immunoelectron microscopy, indicated that the enzyme is mainly located in the cytoplasm of both wild-type cells and transfectants. Digitonin titration experiments also confirmed this observation. Hence, while the initial step of isoprenoid biosynthesis catalyzed by 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase is located in the mitochondrion, synthesis of farnesyl diphosphate by farnesyl diphosphate synthase is a cytosolic process. Leishmania major promastigote transfectants overexpressing farnesyl diphosphate synthase were highly resistant to risedronate, and the degree of resistance correlated with the increase in enzyme activity. Likewise, when resistance was induced by stepwise selection with the drug, the resulting resistant promastigotes exhibited increased levels of farnesyl diphosphate synthase. The overproduction of protein under different conditions of exposure to risedronate further supports the hypothesis that this enzyme is the main target of aminobisphosphonates in Leishmania cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The intracellular target for the antiresorptive aminobisphosphonate drugs in Dictyostelium discoideum is the enzyme farnesyl diphosphate synthase.J Bone Miner Res. 2000 May;15(5):971-81. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2000.15.5.971. J Bone Miner Res. 2000. PMID: 10804029
-
Intracellular location of the early steps of the isoprenoid biosynthetic pathway in the trypanosomatids Leishmania major and Trypanosoma brucei.Int J Parasitol. 2009 Feb;39(3):307-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2008.08.012. Epub 2008 Sep 27. Int J Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 18848949
-
Alendronate is a specific, nanomolar inhibitor of farnesyl diphosphate synthase.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000 Jan 1;373(1):231-41. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1999.1502. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000. PMID: 10620343
-
Anti-infectives targeting the isoprenoid pathway of Toxoplasma gondii.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008 Mar;12(3):253-63. doi: 10.1517/14728222.12.3.253. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008. PMID: 18269336 Review.
-
[Research progress on the squalene synthase].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2003 Oct;43(5):676-80. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2003. PMID: 16281569 Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Identifying Structural Determinants of Product Specificity in Leishmania major Farnesyl Diphosphate Synthase.Biochemistry. 2020 Jul 28;59(29):2751-2759. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00432. Epub 2020 Jul 12. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 32584028 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and thermodynamic basis of the inhibition of Leishmania major farnesyl diphosphate synthase by nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 Mar;70(Pt 3):802-10. doi: 10.1107/S1399004713033221. Epub 2014 Feb 22. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014. PMID: 24598749 Free PMC article.
-
Sterol Biosynthesis Pathway as Target for Anti-trypanosomatid Drugs.Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2009;2009:642502. doi: 10.1155/2009/642502. Epub 2009 Aug 5. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19680554 Free PMC article.
-
Farnesyl diphosphate synthase is involved in the resistance to zoledronic acid of osteosarcoma cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2008 Jun;12(3):928-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00141.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18494934 Free PMC article.
-
Single-target high-throughput transcription analyses reveal high levels of alternative splicing present in the FPPS/GGPPS from Plasmodium falciparum.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 21;5:18429. doi: 10.1038/srep18429. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26688062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergstrom, J. D., R. G. Bostedor, P. J. Masarachia, A. A. Reszka, and G. Rodan. 2000. Alendronate is a specific, nanomolar inhibitor of farnesyl diphosphate synthase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 373:231-241. - PubMed
-
- Biardi, L., and S. K. Krisans. 1996. Compartmentalization of cholesterol biosynthesis. Conversion of mevalonate to farnesyl diphosphate occurs in the peroxisomes. J. Biol. Chem. 271:1784-1788. - PubMed
-
- Bora, D. 1999. Epidemiology of visceral leishmaniasis in India. Natl. Med. J. India 12:62-68. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
-
- Brown, D. L., and R. Robbins. 1999. Developments in the therapeutic applications of bisphosphonates. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 39:651-660. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

