Transcription factor Nrg1 mediates capsule formation, stress response, and pathogenesis in Cryptococcus neoformans
- PMID: 16835458
- PMCID: PMC1489281
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00145-06
Transcription factor Nrg1 mediates capsule formation, stress response, and pathogenesis in Cryptococcus neoformans
Abstract
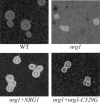
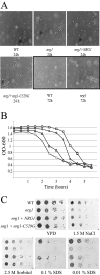
The Cryptococcus neoformans NRG1 gene was identified using gene microarrays to define putative transcription factor genes regulated by the cyclic AMP (cAMP) signal transduction pathway. Disruption of NRG1 results in delayed capsule formation and mating, two phenotypes that are directly controlled by cAMP signaling. Putative targets of the Nrg1 transcription factor were identified using a second genome microarray to define differences in the transcriptomes of the wild-type and nrg1 mutant strains. These experiments implicate Nrg1 in the transcriptional control of multiple genes involved in carbohydrate metabolism and substrate oxidation, as well as the UGD1 gene encoding a UDP-glucose dehydrogenase required for polysaccharide capsule production and cell wall integrity. In addition to being under transcriptional control of the cAMP pathway, Nrg1 contains a putative protein kinase A phosphorylation site; mutation of this motif results in reduced Nrg1 activity. Consistent with prior studies in hypocapsular mutants, the nrg1 mutant strain is attenuated in an animal model of disseminated cryptococcal disease.
Figures



References
-
- Alspaugh, J. A., R. Pukkila-Worley, T. Harashima, L. M. Cavallo, D. Funnell, G. M. Cox, J. R. Perfect, J. W. Kronstad, and J. Heitman. 2002. Adenylyl cyclase functions downstream of the G-alpha protein Gpa1 and controls mating and pathogenicity of Cryptococcus neoformans. Eukaryot. Cell 1:75-84. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Castelli, M. E., E. Garcia Vescovi, and F. C. Soncini. 2000. The phosphatase activity is the target for Mg2+ regulation of the sensor protein PhoQ in Salmonella. J. Biol. Chem. 275:22948-22954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

