Expression of CD8alpha identifies a distinct subset of effector memory CD4+ T lymphocytes
- PMID: 16836648
- PMCID: PMC1782346
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02428.x
Expression of CD8alpha identifies a distinct subset of effector memory CD4+ T lymphocytes
Abstract
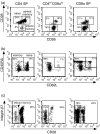
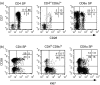
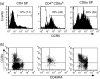
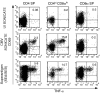
Circulating CD4+ CD8+ T lymphocytes have been described in the peripheral blood of humans and several animal species. However, the origin and functional properties of these cells remain poorly understood. In the present study, we evaluated the frequency, phenotype and function of peripheral CD4+ CD8+ T cells in rhesus macaques. Two distinct populations of CD4+ CD8+ T cells were identified: the dominant one was CD4hi CD8lo and expressed the CD8alphaalpha homodimer, while the minor population was CD4lo CD8hi and expressed the CD8alphabeta heterodimer. The majority of CD4hi CD8alphalo T cells exhibited an activated effector/memory phenotype (CCR5lo CD7- CD28- HLA-DR+) and expressed relatively high levels of granzyme B. Intracellular cytokine staining assays demonstrated that the frequency of cytomegalovirus-specific T cells was enriched five-fold in CD4hi CD8alphalo T cells compared to single-positive CD4+ T cells, whereas no consistent enrichment was observed for simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-specific T cells. Cross-sectional studies of SIV-infected animals demonstrated that the frequency of CD4hi CD8alphalo T cells was lower in wild-type SIV-infected animals compared to uninfected controls, although prospective studies of SIV-infected animals demonstrated depletion of CD4hi CD8alphalo lymphocytes only in a subset of animals. Taken together, these data suggest that CD4+ T cells expressing CD8alpha represent an effector/memory subset of CD4+ T cells and that this cell population can be depleted during the course of SIV infection.
Figures


Comment in
-
CD4+ CD8+ T cells in young and elderly humans. Comment on Macchia I, Gauduin MC, Kaur A, Johnson RP. Expression of CD8alpha identifies a distinct subset of effector memory CD4 T lymphocytes. Immunology 2006; 119:232-42.Immunology. 2007 Mar;120(3):292-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02542.x. Immunology. 2007. PMID: 17313653 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Differential CD4+ T-lymphocyte apoptosis and bystander T-cell activation in rhesus macaques and sooty mangabeys during acute simian immunodeficiency virus infection.J Virol. 2009 Jan;83(2):572-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01715-08. Epub 2008 Nov 5. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 18987149 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of a virus-specific effector-memory CD4+ T cell response by attenuated SIV infection.J Exp Med. 2006 Nov 27;203(12):2661-72. doi: 10.1084/jem.20060134. Epub 2006 Nov 20. J Exp Med. 2006. PMID: 17116733 Free PMC article.
-
Activated memory CD4(+) T helper cells repopulate the intestine early following antiretroviral therapy of simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus macaques but exhibit a decreased potential to produce interleukin-2.J Virol. 1999 Aug;73(8):6661-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.8.6661-6669.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10400763 Free PMC article.
-
Development of circulating CD4+ T-cell memory.Immunol Cell Biol. 2019 Aug;97(7):617-624. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12272. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Immunol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31120158 Review.
-
The Naming of Memory T-Cell Subsets.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2021 Jan 4;13(1):a037788. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a037788. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2021. PMID: 33229439 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intravenous BCG-mediated protection against tuberculosis requires CD4+ T cells and CD8α+ lymphocytes.J Exp Med. 2025 Apr 7;222(4):e20241571. doi: 10.1084/jem.20241571. Epub 2025 Feb 6. J Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 39912921 Free PMC article.
-
Rhesus CMV: an emerging animal model for human CMV.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008 Jun;197(2):109-15. doi: 10.1007/s00430-007-0073-y. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18193454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of the immune system of Ellegaard Göttingen Minipigs - An important large animal model in experimental medicine.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 20;13:1003986. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1003986. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36203585 Free PMC article.
-
CD8 T cell response maturation defined by anentropic specificity and repertoire depth correlates with SIVΔnef-induced protection.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Feb 17;11(2):e1004633. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004633. eCollection 2015 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25688559 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent Low-Level Replication of SIVΔnef Drives Maturation of Antibody and CD8 T Cell Responses to Induce Protective Immunity against Vaginal SIV Infection.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Dec 13;12(12):e1006104. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006104. eCollection 2016 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27959961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blue ML, Daley JF, Levine H, Schlossman SF. Co-expression of T4 and T8 on peripheral blood T cells demonstrated by two-color fluorescence flow cytometry. J Immunol. 1985;134:228–34. - PubMed
-
- Lanier LL, Phillips JH. Evidence for three types of human cytotoxic lymphocytes. Immunol Today. 1986;7:132–4. - PubMed
-
- Ortolani C, Forti E, Radin E, Cibin R, Cossarizza A. Cytofluorimetric identification of two populations of double positive (CD4+ CD8+) T lymphocytes in human peripheral blood. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;191:601–9. - PubMed
-
- Colombatti A, Doliana R, Schiappacassi M, Argentini C, Tonutti E, Feruglio C, Sala P. Age-related persistent clonal expansions of CD28(–) cells: phenotypic and molecular TCR analysis reveals both CD4(+) and CD4(+) CD8(+) cells with identical CDR3 sequences. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1998;89:61–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

