Electrophoresis of proteins and DNA on horizontal sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels
- PMID: 16836743
- PMCID: PMC1538630
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4933-3-7
Electrophoresis of proteins and DNA on horizontal sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels
Abstract
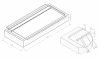
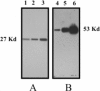
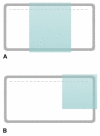
An inexpensive Plexiglas apparatus which allows a simple and rapid preparation of horizontal polyacrylamide gels of different dimensions for different purposes, is described. Preparation of such gels is as easy and rapid as agarose gel preparation, and polymerized polyacrylamide gels are used to fractionate proteins or small DNA fragments using a common horizontal electrophoretic tank. This apparatus was used to electrophoretically fractionate proteins or DNA for immuno-blot analyses, particularly in the study of the allergenic response to Parietaria judaica pollen in senescence, for Southern-blot hybridizations and in the study of DNA polymorphisms.
Figures


References
-
- Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 2. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY; 1989.
-
- Hawcroft DM. Electrophoresis: the basics. IRL Press at Oxford University Press; 1997.
-
- Harlow E, Lane D. Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY; 1988.
-
- Zhu J, Rogers AV, Burke-Gaffney A, Hellewell PG, Jeffery PK. Cytokine-induced airway epithelial ICAM-1 upregulation: quantification by high-resolution scanning and transmission electron microscopy. Eur Respir J. 1999;13:1318–1328. - PubMed
-
- Duro G, Colombo P, Costa MA, Izzo V, Porcasi R, Di Fiore R, Locorotondo G, Mirisola GM, Cocchiara R, Geraci D. cDNA cloning, sequence analysis and allergological characterization of Par j 2.0101, a new major allergen of the Parietaria judaica pollen. FEBS Letters. 1996;399:295–298. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(96)01328-2. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

