Tickborne encephalitis virus, Norway and Denmark
- PMID: 16836835
- PMCID: PMC3291057
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1207.051567
Tickborne encephalitis virus, Norway and Denmark
Abstract
Serum from 2 Norwegians with tickborne encephalitis (TBE) (1 of whom was infected in Denmark) and 810 Norwegian ticks were tested for TBE virus (TBEV) RNA by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Sequencing and phylogenetic analysis were performed. This is the first genome detection of TBEV in serum from Norwegian patients.
Figures
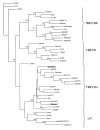
References
-
- Fauquet CM. Virus taxonomy: VIII report of the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press; 2005. p. 981–8.
-
- Gao GF, Jiang WR, Hussain MH, Venugopal K, Gritsun TS, Reid HW, et al. Sequencing and antigenic studies of a Norwegian virus isolated from encephalomyelitic sheep confirm the existence of louping ill virus outside Great Britain and Ireland. J Gen Virol. 1993;74:109–14. 10.1099/0022-1317-74-1-109 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jensen PM, Skarphedinsson S, Sermenov A. Densities of the tick (Ixodes ricinus) and coexistence of the louping ill virus and tick borne encephalitis virus on the island of Bornholm [article in Danish]. Ugeskr Laeger. 2004;166:2563–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
