Tc-99m pyrophosphate imaging of poloxamer-treated electroporated skeletal muscle in an in vivo rat model
- PMID: 16837135
- PMCID: PMC6139253
- DOI: 10.1016/j.burns.2006.01.011
Tc-99m pyrophosphate imaging of poloxamer-treated electroporated skeletal muscle in an in vivo rat model
Abstract
Objective: This study investigates whether (99m)Tc pyrophosphate (PYP) imaging provides a quantitative non-invasive assessment of the extent of electroporation injury, and of the effect of poloxamer in vivo on electroporated skeletal muscle.
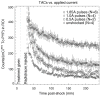
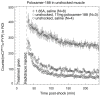
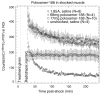
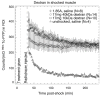
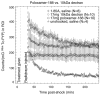
Methods: High-voltage electrical shock was used to produce electroporation injury in an anesthetized rat's hind limb. In each experiment, the injured limb was treated intravenously by either poloxamer-188, dextran, or saline, and subsequently imaged with (99m)Tc PYP. The radiotracer's temporal behavior among the experimental groups was compared using curve fitting of time-activity curves from the dynamic image data.
Results: The washout kinetics of (99m)Tc PYP changed in proportion to the electric current magnitude that produced electroporation. Also, (99m)Tc PYP washout from electroporated muscle differed between poloxamer-188 treatment and saline treatment. Finally, 10-kDa dextran treatment of electroporated muscle altered (99m)Tc PYP washout less than poloxamer-188 treatment.
Conclusions: Behavior of (99m)Tc PYP in electroporated muscle appears to be an indicator of the amount of electroporation injury. Compared to saline, intravenous polaxamer-188 treatment reduced the amount of (99m)Tc PYP uptake. Coupled to results showing poloxamer-188 seals ruptured cellular membranes, lessens the extent of electroporation injury and improves cell viability, (99m)Tc PYP imaging appears to be a useful in vivo monitoring tool for the extent of electroporation injury.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural and functional recovery of electropermeabilized skeletal muscle in-vivo after treatment with surfactant poloxamer 188.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 May;1768(5):1238-46. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.01.012. Epub 2007 Jan 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17382288 Free PMC article.
-
High-voltage electric injury: assessment of muscle viability with MR imaging and Tc-99m pyrophosphate scintigraphy.Radiology. 1995 Apr;195(1):205-10. doi: 10.1148/radiology.195.1.7892470. Radiology. 1995. PMID: 7892470
-
Non-invasive detection and differentiation of cardiac amyloidosis using 99mTc-pyrophosphate scintigraphy and 11C-Pittsburgh compound B PET imaging.Amyloid. 2020 Dec;27(4):266-274. doi: 10.1080/13506129.2020.1798223. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Amyloid. 2020. PMID: 32722948
-
The use of Technetium-99 pyrophosphate scanning in management of high voltage electrical injuries.Am Surg. 1994 Nov;60(11):886-8. Am Surg. 1994. PMID: 7978687 Clinical Trial.
-
Towards a Diagnosis of Cardiac Amyloidosis: Single Center Experience with 99m Technetium Pyrophosphate Planar Imaging and Opportunities for Standardization of Diagnostic Workflow.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Feb 16;59(2):378. doi: 10.3390/medicina59020378. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 36837580 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Poloxamer-Based Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Review.Gels. 2022 Jun 8;8(6):360. doi: 10.3390/gels8060360. Gels. 2022. PMID: 35735704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and functional recovery of electropermeabilized skeletal muscle in-vivo after treatment with surfactant poloxamer 188.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 May;1768(5):1238-46. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.01.012. Epub 2007 Jan 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17382288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernstein T. Electrical injury: Electrical engineer’s perspective and an historical review. In: Lee RC, Capelli-Schellpfeffer M, Kelly KM, editors. Ann NY Acad Sci. Vol. 720. 1994. pp. 1–10. Electrical injury: a multidisciplinary approach to therapy, prevention, and rehabilitation. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Cravalho EG, Burke JF. Electrical trauma: the pathophysiology, manifestations, and clinical management. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1992.
-
- Reilly JP. Scales of reaction to electric shock. In: Lee RC, Capelli-Schellpfeffer M, Kelly KM, editors. Ann NY Acad Sci. Vol. 720. 1994. pp. 21–37. Electrical injury: a multidisciplinary approach to therapy, prevention, and rehabilitation. - PubMed
-
- Kelley KM, Pliskin N, Meyer G, Lee RC. Neuropsychiatric aspects of electrical injury: The nature of psychiatric disturbance. In: Lee RC, Capelli-Schellpfeffer M, Kelly KM, editors. Ann NY Acad Sci. Vol. 720. 1994. pp. 213–8. Electrical injury: a multi-disciplinary approach to therapy, prevention, and rehabilitation. - PubMed
-
- Duff K, McCaffrey RJ. Electrical injury and lightning injury: a review of their mechanisms and neuropsychological, psychiatric, and neurological sequalae. Neuropsychol Rev. 2001;11:101–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

