Etanercept maintains the clinical benefit achieved by infliximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who discontinued infliximab because of side effects
- PMID: 16837489
- PMCID: PMC1798487
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.058776
Etanercept maintains the clinical benefit achieved by infliximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who discontinued infliximab because of side effects
Erratum in
- Ann Rheum Dis. 2007 Jun;66(6):847. Monteccuco, Carlomaurizio [corrected to Montecucco, Carlomaurizio]
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of switching to etanercept treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who already responded to infliximab, but presented side effects.
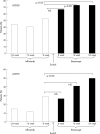
Methods: Charts of 553 patients with rheumatoid arthritis were retrospectively reviewed to select patients who responded to the treatment with infliximab and switched to etanercept because of occurrence of adverse effects. Clinical data were gathered during 24 weeks of etanercept treatment and for the same period of infliximab treatment before infliximab was stopped. Disease Activity Score computed on 44 joints (DAS-44), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) 1st hour, Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) of pain, Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), and C reactive protein (CRP) were assessed every 8 weeks.
Results: 37 patients were analysed. Adverse events to infliximab were mostly infusion reactions. No statistically significant difference between infliximab, before withdrawal, and etanercept, after 24 weeks, was detected in terms of DAS-44 (2.7 and 1.9, respectively), HAQ (0.75 and 0.75, respectively), ESR (21 and 14, respectively) and CRP (0.5 and 0.3, respectively). VAS pain decreased significantly after switching to etanercept treatment (40 and 24, respectively; p<0.05).
Conclusions: Our study shows that etanercept maintains the clinical benefit achieved by infliximab, and suggests that a second tumour necrosis factor (TNF) alpha inhibitor can be the favourable treatment for rheumatoid arthritis when the first TNFalpha blocker has been withdrawn because of adverse events.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
[Etanercept in rheumatoid arthritis patients with a poor therapeutic response to infliximab].Med Clin (Barc). 2004 Mar 13;122(9):321-4. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7753(04)74223-2. Med Clin (Barc). 2004. PMID: 15033049 Clinical Trial. Spanish.
-
[Clinical experience with TNF-alpha inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis].Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2005 Jun 16;125(12):1664-6. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2005. PMID: 15976836 Norwegian.
-
Treatment with tumour necrosis factor alpha antagonists in patients with rheumatoid arthritis induces anticardiolipin antibodies.Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Sep;63(9):1075-8. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.018093. Epub 2004 Apr 5. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004. PMID: 15066863 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-TNF agents for rheumatoid arthritis.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2001 Mar;51(3):201-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2001.00321.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11298065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Switching between TNFalpha antagonists in rheumatoid arthritis: personal experience and review of the literature.Reumatismo. 2009 Apr-Jun;61(2):107-17. doi: 10.4081/reumatismo.2009.107. Reumatismo. 2009. PMID: 19633797 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the efficacy of sequential biologic therapies for rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors.Arthritis Res Ther. 2011 Feb 16;13(1):R25. doi: 10.1186/ar3249. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 21324169 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of switching anti-TNF drugs in rheumatoid arthritis--a study based on observational data from the Finnish Register of Biological Treatment (ROB-FIN).Clin Rheumatol. 2011 Nov;30(11):1447-54. doi: 10.1007/s10067-011-1779-1. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Clin Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21644062
-
The effect of neutralizing antibodies on the sustainable efficacy of biologic therapies: what's in it for African and Middle Eastern rheumatologists.Clin Rheumatol. 2012 Sep;31(9):1281-7. doi: 10.1007/s10067-012-2040-2. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Clin Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22875700 Review.
-
Abatacept: a T-cell co-stimulation modulator for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2008 Nov;27(11):1343-53. doi: 10.1007/s10067-008-0964-3. Epub 2008 Aug 1. Clin Rheumatol. 2008. PMID: 18670735 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical application and evaluation of anti-TNF-alpha agents for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 Sep;31(9):1133-40. doi: 10.1038/aps.2010.134. Epub 2010 Aug 16. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010. PMID: 20711219 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mpofu S, Fatima F, Moots R J. Anti‐TNF‐alpha therapies: they are all the same (aren't they?). Rheumatology (Oxford) 200544271–273. - PubMed
-
- Delaunay C, Farrenq V, Marini‐Portugal A, Cohen J D, Chevalier X, Claudepierre P. Infliximab to etanercept switch in patients with spondyloarthropathies and psoriatic arthritis: preliminary data. J Rheumatol 2005322183–2185. - PubMed
-
- Wick M C, Ernestam S, Lindblad S, Bratt J, Klareskog L, van Vollenhoven R F. Adalimumab (Humira) restores clinical response in patients with secondary loss of efficacy from infliximab (Remicade) or etanercept (Enbrel): results from the STURE registry at Karolinska University Hospital. Scand J Rheumatol 200534353–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous