Neuronal calcium sensor-1 and phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta stimulate extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling by accelerating recycling through the endocytic recycling compartment
- PMID: 16837555
- PMCID: PMC1593177
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-11-1014
Neuronal calcium sensor-1 and phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta stimulate extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling by accelerating recycling through the endocytic recycling compartment
Abstract
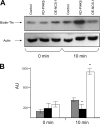
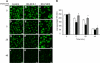
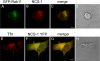
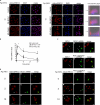
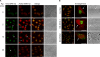
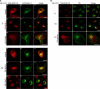
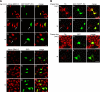
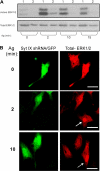
We demonstrate that recycling through the endocytic recycling compartment (ERC) is an essential step in Fc epsilonRI-induced activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2. We show that ERK1/2 acquires perinuclear localization and colocalizes with Rab 11 and internalized transferrin in Fc epsilonRI-activated cells. Moreover, a close correlation exists between the amount of ERC-localized ERK1/2 and the amount of phospho-ERK1/2 that resides in the nucleus. We further show that by activating phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta (PI4Kbeta) and increasing the cellular level of phosphatidylinositol(4) phosphate, neuronal calcium sensor-1 (NCS-1), a calmodulin-related protein, stimulates recycling and thereby enhances Fc epsilonRI-triggered activation and nuclear translocation of ERK1/2. Conversely, NCS-1 short hairpin RNA, a kinase dead (KD) mutant of PI4Kbeta (KD-PI4Kbeta), the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of FAPP1 as well as RNA interference of synaptotagmin IX or monensin, which inhibit export from the ERC, abrogate Fc epsilonRI-induced activation of ERK1/2. Consistently, NCS-1 also enhances, whereas both KD-PI4Kbeta and FAPP1-PH domain inhibit, Fc epsilonRI-induced release of arachidonic acid/metabolites, a downstream target of ERK1/2 in mast cells. Together, our results demonstrate a novel role for NCS-1 and PI4Kbeta in regulating ERK1/2 signaling and inflammatory reactions in mast cells. Our results further identify the ERC as a crucial determinant in controlling ERK1/2 signaling.
Figures

References
-
- Birkeland H. C., Stenmark H. Protein targeting to endosomes and phagosomes via FYVE and PX domains. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004;282:89–115. - PubMed
-
- Bourne Y., Dannenberg J., Pollmann V., Marchot P., Pongs O. Immunocytochemical localization and crystal structure of human frequenin (neuronal calcium sensor 1). J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:11949–11955. - PubMed
-
- Braunewell K. H., Gundelfinger E. D. Intracellular neuronal calcium sensor proteins: a family of EF-hand calcium-binding proteins in search of a function. Cell Tissue Res. 1999;295:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Carpentier J. L., Dayer J. M., Lang U., Silverman R., Orci L., Gorden P. Down-regulation and recycling of insulin receptors. Effect of monensin on IM-9 lymphocytes and U-937 monocyte-like cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1984;259:14190–14195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

