Endogenous alpha-synuclein is induced by valproic acid through histone deacetylase inhibition and participates in neuroprotection against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity
- PMID: 16837598
- PMCID: PMC6674182
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0096-06.2006
Endogenous alpha-synuclein is induced by valproic acid through histone deacetylase inhibition and participates in neuroprotection against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity
Abstract
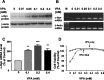
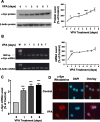
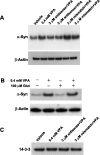
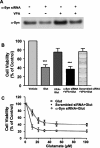
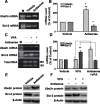
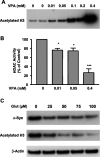
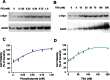
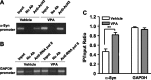
Emerging evidence suggests that alpha-synuclein (alpha-syn), which is traditionally thought to have a pathophysiological role in neurodegenerative diseases, can have neuroprotective effects. This study aimed to investigate whether endogenous alpha-syn in neurons can be induced by valproic acid (VPA), a mood-stabilizer, anticonvulsant and histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, and if so, whether the alpha-syn induction is neuroprotective. VPA treatment of rat cerebellar granule cells caused a robust dose- and time-dependent increase in levels of alpha-syn protein and mRNA and in the intensity of alpha-syn immunostaining. Knockdown of VPA-induced alpha-syn overexpression with alpha-syn antisense oligonucleotides or siRNA completely blocked VPA-induced neuroprotection. alpha-Syn knockdown also exacerbated glutamate neurotoxicity, stimulated the expression of the proapoptotic gene ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2N, and downregulated the expression of the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2. Induction of alpha-syn by VPA was associated with inhibition of HDAC activity, resulting in hyperacetylation of histone H3 in the alpha-syn promoter and a marked increase in alpha-syn promoter activity. Moreover, VPA-induced alpha-syn induction and neuroprotection were mimicked by HDAC inhibitors sodium 4-phenylbutyrate and trichostatin A (TSA). alpha-syn was also induced by VPA in rat cerebral cortical neurons. Additionally, treatment of rats with VPA, sodium butyrate, or TSA markedly increased alpha-syn protein levels in the cortex and cerebellum. Together, our results demonstrate for the first time that VPA induces alpha-syn in neurons through inhibition of HDAC and that this alpha-syn induction is critically involved in neuroprotection against glutamate excitotoxicity. Clinically, VPA may represent a suitable treatment for excitotoxicity-related neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Valproic acid, a mood stabilizer and anticonvulsant, protects rat cerebral cortical neurons from spontaneous cell death: a role of histone deacetylase inhibition.FEBS Lett. 2003 May 8;542(1-3):74-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00350-8. FEBS Lett. 2003. PMID: 12729901
-
Synergistic neuroprotective effects of lithium and valproic acid or other histone deacetylase inhibitors in neurons: roles of glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition.J Neurosci. 2008 Mar 5;28(10):2576-88. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5467-07.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18322101 Free PMC article.
-
Valproic acid induces functional heat-shock protein 70 via Class I histone deacetylase inhibition in cortical neurons: a potential role of Sp1 acetylation.J Neurochem. 2009 Nov;111(4):976-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06385.x. Epub 2009 Sep 18. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19765194 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical, molecular and epigenetic mechanisms of valproic acid neuroprotection.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2009 Jan;2(1):95-109. doi: 10.2174/1874467210902010095. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 20021450 Review.
-
Potential roles of HDAC inhibitors in mitigating ischemia-induced brain damage and facilitating endogenous regeneration and recovery.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(28):5105-20. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319280009. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23448466 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive review on pharmacological applications and drug-induced toxicity of valproic acid.Saudi Pharm J. 2023 Feb;31(2):265-278. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2022.12.001. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Saudi Pharm J. 2023. PMID: 36942277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective effects of the mood stabilizer lamotrigine against glutamate excitotoxicity: roles of chromatin remodelling and Bcl-2 induction.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013 Apr;16(3):607-20. doi: 10.1017/S1461145712000429. Epub 2012 May 8. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 22564541 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylases and their inhibitors in cancer, neurological diseases and immune disorders.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014 Sep;13(9):673-91. doi: 10.1038/nrd4360. Epub 2014 Aug 18. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014. PMID: 25131830 Review.
-
Phenylbutyrate-a pan-HDAC inhibitor-suppresses proliferation of glioblastoma LN-229 cell line.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jan;37(1):931-42. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3781-8. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26260271 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial effects of mood stabilizers lithium, valproate and lamotrigine in experimental stroke models.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011 Dec;32(12):1433-45. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.140. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011. PMID: 22056617 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albani D, Peverelli E, Rametta R, Batelli S, Veschini L, Negro A, Forloni G (2004). Protective effect of TAT-delivered alpha-synuclein: relevance of the C-terminal domain and involvement of HSP70. FASEB J 18:1713–1715. - PubMed
-
- Alves da Costa CA, Ancolio K, Checler F (2000). Wild-type but not Parkinson’s disease-related Ala-53→Thr mutant α-synuclein protects neuronal cells from apoptotic stimuli. J Biol Chem 275:24065–24069. - PubMed
-
- Alves da Costa CA, Paitel E, Vincent B, Checler F (2002). α-synuclein lowers p53-dependent apoptotic response of neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 277:50980–50984. - PubMed
-
- Bantounas I, Phylactou LA, Uney JB (2004). RNA interference and the use of small interfering RNA to study gene function in mammalian systems. J Mol Endocrinol 33:545–557. - PubMed
-
- Borghi R, Marchese R, Negro A, Marinelli L, Forloni G, Zaccheo D, Abbruzzese G, Tabaton M (2000). Full length alpha-Synuclein is present in cerebrospinal fluid from Parkinson’s disease and normal subjects. Neurosci Lett 287:65–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
