Clarifying the mechanics of DNA strand exchange in meiotic recombination
- PMID: 16838012
- PMCID: PMC5607947
- DOI: 10.1038/nature04885
Clarifying the mechanics of DNA strand exchange in meiotic recombination
Abstract
During meiosis, accurate separation of maternal and paternal chromosomes requires that they first be connected to one another through homologous recombination. Meiotic recombination has many intriguing but poorly understood features that distinguish it from recombination in mitotically dividing cells, and several of these features depend on the meiosis-specific DNA strand exchange protein Dmc1 (disrupted meiotic cDNA1). Many questions about this protein have arisen since its discovery more than a decade ago, but recent genetic and biochemical breakthroughs promise to shed light on the unique behaviours and functions of this central player in the remarkable chromosome dynamics of meiosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
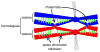
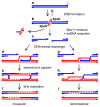

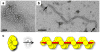
Similar articles
-
Human meiotic recombinase Dmc1 promotes ATP-dependent homologous DNA strand exchange.Nature. 2004 May 27;429(6990):433-7. doi: 10.1038/nature02563. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15164066
-
Meiotic recombination: sealing the partnership at the junction.Curr Biol. 2004 Nov 23;14(22):R962-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.10.043. Curr Biol. 2004. PMID: 15556855 Review.
-
Mnd1/Hop2 facilitates Dmc1-dependent interhomolog crossover formation in meiosis of budding yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;26(8):2913-23. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.8.2913-2923.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16581767 Free PMC article.
-
DNA strand exchange activity of rice recombinase OsDmc1 monitored by fluorescence resonance energy transfer and the role of ATP hydrolysis.FEBS J. 2006 Apr;273(7):1497-506. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05170.x. FEBS J. 2006. PMID: 16689935
-
Roles of RecA homologues Rad51 and Dmc1 during meiotic recombination.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004;107(3-4):201-7. doi: 10.1159/000080598. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15467365 Review.
Cited by
-
Homologous Recombination and Repair Functions Required for Mutagenicity during Yeast Meiosis.Genes (Basel). 2023 Oct 28;14(11):2017. doi: 10.3390/genes14112017. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38002960 Free PMC article.
-
Human PSF concentrates DNA and stimulates duplex capture in DMC1-mediated homologous pairing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Apr;40(7):3031-41. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1229. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22156371 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage response is suppressed by the high cyclin-dependent kinase 1 activity in mitotic mammalian cells.J Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 14;286(41):35899-35905. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.267690. Epub 2011 Aug 30. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21878640 Free PMC article.
-
SHOC1 is a ERCC4-(HhH)2-like protein, integral to the formation of crossover recombination intermediates during mammalian meiosis.PLoS Genet. 2018 May 9;14(5):e1007381. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007381. eCollection 2018 May. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29742103 Free PMC article.
-
PRDM9 binding organizes hotspot nucleosomes and limits Holliday junction migration.Genome Res. 2014 May;24(5):724-32. doi: 10.1101/gr.170167.113. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Genome Res. 2014. PMID: 24604780 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Petronczki M, Siomos MF, Nasmyth K. Un menage a quatre: the molecular biology of chromosome segregation in meiosis. Cell. 2003;112:423–440. - PubMed
-
- Kleckner N. Chiasma formation: chromatin/axis interplay and the role(s) of the synaptonemal complex. Chromosoma. 2006;115:175–194. - PubMed
-
- Keeney S. Mechanism and control of meiotic recombination initiation. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2001;52:1–53. - PubMed
-
- Bianco PR, Tracy RB, Kowalczykowski SC. DNA strand exchange proteins: a biochemical and physical comparison. Front Biosci. 1998;3:D570–603. - PubMed
-
- Shinohara A, Shinohara M. Roles of RecA homologues Rad51 and Dmc1 during meiotic recombination. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004;107:201–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

