Selective inhibition of the human tie-1 promoter with triplex-forming oligonucleotides targeted to Ets binding sites
- PMID: 16838069
- PMCID: PMC1514554
- DOI: 10.2119/2005-00046.Hewett
Selective inhibition of the human tie-1 promoter with triplex-forming oligonucleotides targeted to Ets binding sites
Abstract
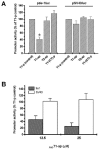
The Tie receptors (Tie-1 and Tie-2/Tek) are essential for angiogenesis and vascular remodeling/integrity. Tie receptors are up-regulated in tumor-associated endothelium, and their inhibition disrupts angiogenesis and can prevent tumor growth as a consequence. To investigate the potential of anti-gene approaches to inhibit tie gene expression for anti-angiogenic therapy, we have examined triple-helical (triplex) DNA formation at 2 tandem Ets transcription factor binding motifs (designated E-1 and E-2) in the human tie-1 promoter. Various tie-1 promoter deletion/mutation luciferase reporter constructs were generated and transfected into endothelial cells to examine the relative activities of E-1 and E-2. The binding of antiparallel and parallel (control) purine motif oligonucleotides (21-22 bp) targeted to E-1 and E-2 was assessed by plasmid DNA fragment binding and electrophoretic mobility shift assays. Triplex-forming oligonucleotides were incubated with tie-1 reporter constructs and transfected into endothelial cells to determine their activity. The Ets binding motifs in the E-1 sequence were essential for human tie-1 promoter activity in endothelial cells, whereas the deletion of E-2 had no effect. Antiparallel purine motif oligonucleotides targeted at E-1 or E-2 selectively formed strong triplex DNA (K(d) approximately 10(-7) M) at 37 degrees C. Transfection of tie-1 reporter constructs with triplex DNA at E-1, but not E-2, specifically inhibited tie-1 promoter activity by up to 75% compared with control oligonucleotides in endothelial cells. As similar multiple Ets binding sites are important for the regulation of several endothelial-restricted genes, this approach may have broad therapeutic potential for cancer and other pathologies involving endothelial proliferation/dysfunction.
Figures



References
-
- Talks KL, Harris AL. The current status of anti-angiogenic factors. Br J Haematol. 2000;109:477–89. - PubMed
-
- Veikkola T, Karkkainen M, Claesson-Welsh L, Alitalo K. Regulation of angiogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Cancer Res. 2000;60:203–12. - PubMed
-
- Sato TN, et al. Distinct roles of the receptor tyrosine kinases Tie-1 and Tie-2 in blood vessel formation. Nature. 1996;376:70–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
