Informational masking of speech in children: auditory-visual integration
- PMID: 16838537
- PMCID: PMC2858977
- DOI: 10.1121/1.2195121
Informational masking of speech in children: auditory-visual integration
Abstract
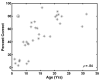
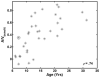
The focus of this study was the release from informational masking that could be obtained in a speech task by viewing a video of the target talker. A closed-set speech recognition paradigm was used to measure informational masking in 23 children (ages 6-16 years) and 10 adults. An audio-only condition required attention to a monaural target speech message that was presented to the same ear with a time-synchronized distracter message. In an audiovisual condition, a synchronized video of the target talker was also presented to assess the release from informational masking that could be achieved by speechreading. Children required higher target/distracter ratios than adults to reach comparable performance levels in the audio-only condition, reflecting a greater extent of informational masking in these listeners. There was a monotonic age effect, such that even the children in the oldest age group (12-16.9 years) demonstrated performance somewhat poorer than adults. Older children and adults improved significantly in the audiovisual condition, producing a release from informational masking of 15 dB or more in some adult listeners. Audiovisual presentation produced no informational masking release for the youngest children. Across all ages, the benefit of a synchronized video was strongly associated with speechreading ability.
Figures
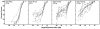
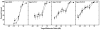




References
-
- Allen P, Wightman F. Psychometric functions for children's detection of tones in noise. J Speech Hear Res. 1994;37:205–215. - PubMed
-
- Allen P, Wightman F. Effects of signal and masker uncertainty on children's detection. J Speech Hear Res. 1995;38:503–511. - PubMed
-
- Allen P, Wightman F, Kistler D, Dolan T. Frequency resolution in children. J Speech Hear Res. 1989;32:317–322. - PubMed
-
- Arbogast TL, Mason CR, Kidd G., Jr The effect of spatial separation on informational and energetic masking of speech. J Acoust Soc Am. 2002;112:2086–2098. - PubMed
-
- Arbogast TL, Mason CR, Kidd G., Jr The effect of spatial separation on informational masking of speech in normal-hearing and hearing-impaired listeners. J Acoust Soc Am. 2005;117:2169–2180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

