Live attenuated B. pertussis as a single-dose nasal vaccine against whooping cough
- PMID: 16839199
- PMCID: PMC1487175
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020065
Live attenuated B. pertussis as a single-dose nasal vaccine against whooping cough
Abstract
Pertussis is still among the principal causes of death worldwide, and its incidence is increasing even in countries with high vaccine coverage. Although all age groups are susceptible, it is most severe in infants too young to be protected by currently available vaccines. To induce strong protective immunity in neonates, we have developed BPZE1, a live attenuated Bordetella pertussis strain to be given as a single-dose nasal vaccine in early life. BPZE1 was developed by the genetic inactivation or removal of three major toxins. In mice, BPZE1 was highly attenuated, yet able to colonize the respiratory tract and to induce strong protective immunity after a single nasal administration. Protection against B. pertussis was comparable to that induced by two injections of acellular vaccine (aPV) in adult mice, but was significantly better than two administrations of aPV in infant mice. Moreover, BPZE1 protected against Bordetella parapertussis infection, whereas aPV did not. BPZE1 is thus an attractive vaccine candidate to protect against whooping cough by nasal, needle-free administration early in life, possibly at birth.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

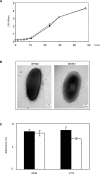
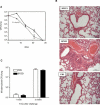
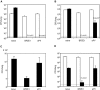
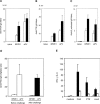
References
-
- World Health Organization [WHO] The world health report 2004—Changing history. Geneva: WHO; 2004. Available: http://www.who.int/whr/2004/en. Accessed 31 May 2006.
-
- Das P. Whooping cough makes global comeback. Lancet Infect Dis. 2002;2:322. - PubMed
-
- Tan T, Trindade E, Skowronski D. Epidemiology of pertussis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005;24:S10–S18. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Pertussis. Available: http://www.cdc.gov/nip/publications/pink/pert.pdf. Accessed 31 May 2006.
-
- Wirsing von König CH, Halperin S, Riffelmann M, Guiso N. Pertussis of adults and infants. Lancet Infect Dis. 2002;2:744–750. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

