EMD: an ensemble algorithm for discovering regulatory motifs in DNA sequences
- PMID: 16839417
- PMCID: PMC1539026
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-342
EMD: an ensemble algorithm for discovering regulatory motifs in DNA sequences
Abstract
Background: Understanding gene regulatory networks has become one of the central research problems in bioinformatics. More than thirty algorithms have been proposed to identify DNA regulatory sites during the past thirty years. However, the prediction accuracy of these algorithms is still quite low. Ensemble algorithms have emerged as an effective strategy in bioinformatics for improving the prediction accuracy by exploiting the synergetic prediction capability of multiple algorithms.
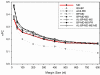
Results: We proposed a novel clustering-based ensemble algorithm named EMD for de novo motif discovery by combining multiple predictions from multiple runs of one or more base component algorithms. The ensemble approach is applied to the motif discovery problem for the first time. The algorithm is tested on a benchmark dataset generated from E. coli RegulonDB. The EMD algorithm has achieved 22.4% improvement in terms of the nucleotide level prediction accuracy over the best stand-alone component algorithm. The advantage of the EMD algorithm is more significant for shorter input sequences, but most importantly, it always outperforms or at least stays at the same performance level of the stand-alone component algorithms even for longer sequences.
Conclusion: We proposed an ensemble approach for the motif discovery problem by taking advantage of the availability of a large number of motif discovery programs. We have shown that the ensemble approach is an effective strategy for improving both sensitivity and specificity, thus the accuracy of the prediction. The advantage of the EMD algorithm is its flexibility in the sense that a new powerful algorithm can be easily added to the system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Limitations and potentials of current motif discovery algorithms.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Sep 2;33(15):4899-913. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki791. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 16284194 Free PMC article.
-
SCOPE: a web server for practical de novo motif discovery.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W259-64. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm310. Epub 2007 May 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17485471 Free PMC article.
-
A cluster refinement algorithm for motif discovery.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2010 Oct-Dec;7(4):654-68. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2009.25. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2010. PMID: 21030733
-
Discovering sequence motifs.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;452:231-51. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-159-2_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18566768 Review.
-
A review on multiple sequence alignment from the perspective of genetic algorithm.Genomics. 2017 Oct;109(5-6):419-431. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2017.06.007. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28669847 Review.
Cited by
-
Promzea: a pipeline for discovery of co-regulatory motifs in maize and other plant species and its application to the anthocyanin and phlobaphene biosynthetic pathways and the Maize Development Atlas.BMC Plant Biol. 2013 Mar 15;13:42. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-13-42. BMC Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 23497159 Free PMC article.
-
MotifClick: prediction of cis-regulatory binding sites via merging cliques.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011 Jun 16;12:238. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-238. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21679436 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and evolution of control logic in prokaryotic transcriptional regulation.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009 Sep;73(3):481-509, Table of Contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00037-08. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19721087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational prediction of conformational B-cell epitopes from antigen primary structures by ensemble learning.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043575. Epub 2012 Aug 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22927994 Free PMC article.
-
A Monte Carlo-based framework enhances the discovery and interpretation of regulatory sequence motifs.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Nov 27;13:317. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-317. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 23181585 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tompa M, Li N, Bailey TL, Church GM, De MB, Eskin E, Favorov AV, Frith MC, Fu Y, Kent WJ, Makeev VJ, Mironov AA, Noble WS, Pavesi G, Pesole G, Regnier M, Simonis N, Sinha S, Thijs G, van HJ, Vandenbogaert M, Weng Z, Workman C, Ye C, Zhu Z. Assessing computational tools for the discovery of transcription factor binding sites. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:137–144. doi: 10.1038/nbt1053. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

