Use of filter paper stored dried blood for measurement of triglycerides
- PMID: 16839425
- PMCID: PMC1540415
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-5-20
Use of filter paper stored dried blood for measurement of triglycerides
Abstract
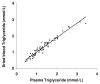
Adaptation of assays on dried blood has advantages of ease of collection, transportation, minimal invasiveness and requirement of small volume. A method for extraction and estimation of triglyceride from blood spots dried on filter paper (Whatman no. 3) has been developed. A single dried blood spot containing 10 muL blood was used. Triglyceride was efficiently extracted in methanol from blood dried on filter paper by incubation at 37 degrees C for two hours with gentle shaking. For the estimation, a commercially available enzymatic method was used. Blood spot assays showed mean intra and inter assay coefficient of variance of 6.0% and 7.4% respectively. A comparison of paired whole blood spots and plasma samples (n = 75, day 0) gave an intraclass correlation of 0.96. The recovery was 99.6%. The dried blood triglyceride concentrations were stable for one month when the filter discs were stored at room temperature (16-28 degrees C). Storage of filters at 4 degrees C extended the stability and triglycerides could be quantitatively recovered after 3 months of storage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of the stability of urea in dried blood spots collected and stored on filter paper.Ann Lab Med. 2013 May;33(3):190-2. doi: 10.3343/alm.2013.33.3.190. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Ann Lab Med. 2013. PMID: 23667845 Free PMC article.
-
Filter paper blood spot assay of human insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-3 and preliminary application in the evaluation of growth hormone status.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998 Jul;83(7):2296-301. doi: 10.1210/jcem.83.7.4923. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998. PMID: 9661598 Clinical Trial.
-
Detection of measles virus RNA in whole blood stored on filter paper.J Med Virol. 2002 Aug;67(4):596-602. doi: 10.1002/jmv.10144. J Med Virol. 2002. PMID: 12116010
-
Utility of dried blood spots for measurement of cholesterol and triglycerides in a surveillance study.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2010 Mar 1;4(2):258-62. doi: 10.1177/193229681000400206. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2010. PMID: 20307386 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid DNA extraction from dried blood spots on filter paper: potential applications in biobanking.Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2014 Dec;5(6):351-7. doi: 10.1016/j.phrp.2014.09.005. Epub 2014 Nov 1. Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2014. PMID: 25562044 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Creatinine measurement and stability in dried serum.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2012 Jul 1;6(4):988-9. doi: 10.1177/193229681200600435. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2012. PMID: 22920830 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comparability of HbA1c and lipids measured with dried blood spot versus venous samples: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Clin Pathol. 2014 May 12;14:21. doi: 10.1186/1472-6890-14-21. eCollection 2014. BMC Clin Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25045323 Free PMC article.
-
The metabolic syndrome and mammographic breast density in a racially diverse and predominantly immigrant sample of women.Cancer Causes Control. 2015 Oct;26(10):1393-403. doi: 10.1007/s10552-015-0630-4. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Cancer Causes Control. 2015. PMID: 26169301 Free PMC article.
-
Antihyperglycemic Activity of Various Fractions of Cassia auriculata Linn. in Alloxan Diabetic Rats.Indian J Pharm Sci. 2008 Mar-Apr;70(2):227-9. doi: 10.4103/0250-474X.41461. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2008. PMID: 20046718 Free PMC article.
-
Dried blood spot collection, sample quality, and fieldwork conditions: Structural validations for conversion into standard values.Am J Hum Biol. 2021 Jul;33(4):e23517. doi: 10.1002/ajhb.23517. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Am J Hum Biol. 2021. PMID: 33063418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hokanson JE, Austin MA. Plasma triglyceride is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease independent of HDL cholesterol level; A Meta analysis of population based prospective studies. J Cardiovasc Risk. 1996;3:213–19. - PubMed
-
- Cook JD, Flowers CH, Skikne BS. An assessment of dried blood spot technology for identifying iron deficiency. Blood. 1998;92:1807–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

