Anti-erbB2 treatment induces cardiotoxicity by interfering with cell survival pathways
- PMID: 16839426
- PMCID: PMC1779483
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr1523
Anti-erbB2 treatment induces cardiotoxicity by interfering with cell survival pathways
Abstract
Introduction: Cardiac dysfunction is among the serious side effects of therapy with recombinant humanized anti-erbB2 monoclonal antibody. The antibody blocks ErbB-2, a receptor tyrosine kinase and co-receptor for other members of the ErbB and epidermal growth factor families, which is over-expressed on the surface of many malignant cells. ErbB-2 and its ligands neuregulin and ErbB-3/ErbB-4 are involved in survival and growth of cardiomyocytes in both postnatal and adult hearts, and therefore the drug may interrupt the correct functioning of the ErbB-2 pathway.
Methods: The effect of the rat-anti-erbB2 monoclonal antibody B-10 was studied in spontaneously beating primary myocyte cultures from rat neonatal hearts. Gene expression was determined by RT-PCR (reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction) and by rat stress-specific microarray analysis, protein levels by Western blot, cell contractility by video motion analysis, calcium transients by the FURA fluorescent method, and apoptosis using the TUNEL (terminal uridine nick-end labelling) assay.
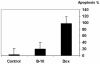
Results: B-10 treatment induces significant changes in expression of 24 out of 207 stress genes analyzed using the microarray technique. Protein levels of ErbB-2, ErbB-3, ErbB-4 and neuregulin decreased after 1 day. However, both transcription and protein levels of ErbB-4 and gp130 increased several fold. Calreticulin and calsequestrin were overexpressed after three days, inducing a decrease in calcium transients, thereby influencing cell contractility. Apoptosis was induced in 20% cells after 24 hours.
Conclusion: Blocking ErbB-2 in cultured rat cardiomyocytes leads to changes that may influence the cell cycle and affects genes involved in heart functions. B-10 inhibits pro-survival pathways and reduces cellular contractility. Thus, it is conceivable that this process may impair the stress response of the heart.
Figures

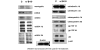

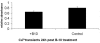

Similar articles
-
Neuregulin-1 beta attenuates doxorubicin-induced alterations of excitation-contraction coupling and reduces oxidative stress in adult rat cardiomyocytes.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006 Nov;41(5):845-54. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2006.08.002. Epub 2006 Sep 26. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 17005195
-
Doxazosin induces activation of GADD153 and cleavage of focal adhesion kinase in cardiomyocytes en route to apoptosis.Cardiovasc Res. 2006 Jul 1;71(1):118-28. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.03.014. Epub 2006 Mar 24. Cardiovasc Res. 2006. PMID: 16631627
-
Inhibition of ErbB2 causes mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiomyocytes: implications for herceptin-induced cardiomyopathy.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004 Dec 7;44(11):2231-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.08.066. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 15582322
-
ErbB receptors, their ligands, and the consequences of their activation and inhibition in the myocardium.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008 May;44(5):831-54. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.02.278. Epub 2008 Mar 4. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18430438 Review.
-
[Monoclonal antibody induces apoptosis against cancer cells].Nihon Rinsho. 2002 Mar;60(3):451-6. Nihon Rinsho. 2002. PMID: 11904957 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Administration of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and β-blockers during adjuvant trastuzumab chemotherapy for nonmetastatic breast cancer: marker of risk or cardioprotection in the real world?Oncologist. 2012;17(7):917-24. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0445. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Oncologist. 2012. PMID: 22673631 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac safety of (neo)adjuvant trastuzumab in the community setting: a single-center experience.Breast Care (Basel). 2014 Apr;9(4):255-60. doi: 10.1159/000365950. Breast Care (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25404884 Free PMC article.
-
ErbB2 overexpression upregulates antioxidant enzymes, reduces basal levels of reactive oxygen species, and protects against doxorubicin cardiotoxicity.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Oct;309(8):H1271-80. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00517.2014. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26254336 Free PMC article.
-
Role of renal function on the development of cardiotoxicity associated with trastuzumab-based adjuvant chemotherapy for early breast cancer.Intern Emerg Med. 2012 Oct;7(5):439-46. doi: 10.1007/s11739-012-0794-9. Epub 2012 Jun 20. Intern Emerg Med. 2012. PMID: 22714882
-
A Growth Tonic for Heart Failure?JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2016 Dec 26;1(7):587-589. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2016.11.002. eCollection 2016 Dec. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2016. PMID: 30167543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alimandi M, Romano A, Curia MC, Muraro R, Fedi P, Aaronson SA, Di Fiore PP, Kraus MH. Cooperative signaling of ErbB3 and ErbB2 in neoplastic transformation and human mammary carcinomas. Oncogene. 1995;10:1813–1821. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987;235:177–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

